ME490
Mechanical
Engineering Lab
Experment # 1
Performance of Centrifugal Fan
UNIVERSITY OF TRIPOLI
Faculty of Engineering-Department of
Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
[email protected]
ME302 Heat Transfer I
1
Contents
• Introduction
• Objective of the Experiment
• Fan Performance Parameters
• Description of Test stand
• What is the Testing Method?
• Data Collection from the Experiment
• How are the results Analyzed?
• How charts are constructed?
• Discussion
Introduction
Fan move air or gases at a constant volume the higher the density of this
medium the more energy is required at a given RPM.
An understanding of the fan parameters and performance helps assure that the
rest of your system process is operating at peak efficiency
Q: Why is testing Fan performance essential to your application?
Ans.: Testing the performance of all manufactured industrial fans, is to
guarantee that the performance curves of your fan use real data and not
theoretical figures. And if your factory or facility installing a new fan or
replacing an older one, and you fell maybe something is wrong with the current
fan, but we can’t quite figure out what it is. Then you need a fan performance
test
Introduction
• A fan performance test helps identify where the fan is operating on
the fan curve or not.
• Do you remember your fluid course? Berolli equation …ect
• What is fan curve ? Fan curve is a graphical representation of the
operational parameters of a fan. Which will be discussed later.
Objective of the Experiment
• There are many objectives which may be summarized them in the
following:
1. To understanding what dose mean by fan performance
2. What is fan parameters
3. To know how to demonstrate the fan performances in curve figures.
4. To know why the companies do fan test performance.
5. To know Tips for Selecting the Perfect Fan
6. To know how to evaluate the fan performance
Fan Performance Parameters
• CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute,
Is essentially how much air your fan can move. It's like measuring how
well your fan can take deep breaths and exhale, circulating air through
your system.
• SP: The Muscle behind the Movement
Static Pressure (SP) is the fan's ability to push air through resistance –
think of it as the force you can put into blowing air through a straw. It's
crucial when the air must move through dense areas like heatsinks or
radiators.
• Why Max RPM Metrics Aren't the Whole Story
• Those impressive max CFM and SP numbers? Your fan won't always
(and shouldn't always) be running at full tilt. Not only that, but every
fan behaves differently at various RPMs.
Description of Test stand
Control Panel Fan Inlet part
Inlet fitting part
Centrifugal Fan
Pt-tube
outlet fitting part
Manometer
Engine Data
outlet duct part
What is the Testing Method?
• To carry out testing, pressure measurements are taken at various points
on the test rigs along with the motor current to determine the exact
airflow throughout the fan’s operating range.
• An important fact to mention, all testing on ACI manufactured fans
show static pressure rather than total pressure
• In other words, we remove the velocity element, which can distort the
final reading. Thus, we ensure that we provide you with the fan’s
actual useable pressure at any given point.
• We can test your fan’s performance at both the inlet and discharge side
and carry out vibration and noise testing if you require.
Position of measuring pressure
Fitting at inlet and outlet
Taking the test data by different
measurement scales
Ampere Reading
Voltage Reading
Fan RPM Reading
Fan RPM Reading
Adjustment
Manometer Reading
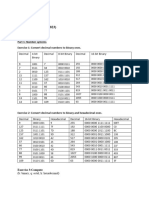
Table No. 1 of Test Reading data
Fan Speed Control
Table No. 2 of Test Reading data
Flowrate Control Valve
Pt-tube reading
Pt-tube reading rig
Velocity Profile inside pipe
How are the result data Analyzed?
Once we have collated all the relevant data, we can then provide you with the test
results and plot your fan’s pressure vs flow curve. The graphical output displays
airflow, pressure, motor current, noise, power, and efficiency.
• Input Parameter: Cd 0.98 dinlet 97 mm g 9.807
m
2
s
kg
kg man 870
air 1.21 3
3 m
m
• Test reading data Analysis
1. Calculating Engine Power from the following formula
Welec I V
2. Calculating ΔP from manometer readings
P man g H
Data Analysis
3. Calculating Volumetric flowrate Qv
2
dinlet 2 Pinlet
Qv Cd
4 air
4. Calculating hydraulic Power:
Whyd Qv Pfan
5. Calculating Fan efficiency:
Whyd
fan
Welec
Final table after the analysis
Calculated Parameter by
Reading test data using Microsoft Excel
Unit transfer
Calculating and Draw Velocity profile inside the duct
2 2
P1 v1 P2 v2 Where: v2 = 0
Z1 Z2
2 g 2 g and Z1 = Z2
Pinlet
v 2
g
How charts are constructed?
• Constructing performance charts involves meticulous testing. Fans are
tested at various RPMs, and measurements of airflow and pressure are
plotted to create these charts.
• These charts show the relationship between CFM, SP, and RPM, providing a
visual representation of a fan’s performance under different conditions.
• INTERPRETING PERFORMANCE CHARTS: WHERE SCIENCE MEETS REAL-
WORLD PERFORMANCE
• When you're looking at a fan performance chart, you're not just seeing
lines and numbers; you're seeing a visual narrative of how a fan will behave
in real-life scenarios. These charts are more than just tools for comparison;
they're the roadmap to understanding a fan's efficiency under varying
conditions.
How charts are constructed?