MAP READING
AND
LAND NAVIGATION
SCOPE OF PRESENTATION
Definition, Importance, Care and Security of Maps
Categories and Types of Maps
Marginal Information
Grids
Scale and Distance
Direction
Elevation and Relief
SCOPE OF PRESENTATION
Navigational Methods and Equipment
Terrain Association
DEFINITION OF MAP
Geographic representation of a portion of the earth’s
surface drawn to scale, as seen from above;
Uses colors, symbols and labels to represent features
found on the ground
IMPORTANCE OF A MAP
1. Strategic and tactical planning in all command;
2. Show relative position on a certain given area;
3. Show accurate distance, location, best routes and key
terrain features
4. Avoid lost and keep alive.
CARE OF MAP
1. Proper folding: Accordion Fold or Slit Fold
2. Carry maps in a water proof pocket and use acetate to
cover the map. Avoid drawing or improper marking to
avoid confusion;
SECURITY OF MAP
1. Maps must not fall into unauthorized hand;
2. When in danger, destroy the map;
3. Avoid indication of plans or area of interest in the map;
CATEGORIES OF MAP
Scale is expressed as a fraction and gives the ratio of map
distance to ground distance
Small 1: 600, 000 and smaller
Medium 1: 600, 000 but smaller than 1:75,000
Large: 1: 75, 000 and larger
TYPES OF MAPS
1. Plain Metric Map
2. Topographic Maps
3. Plastic Relief Map
4. Photo Map
5. Joint Operation Map
6. Pictomap
TYPES OF MAPS
7. Photomosaic
8. Military City Map
9. Special Map
10. Terrain Model
11. Hydrographic Map
MARGINAL INFORMATION
1. Sheet Name – found at the upper center margin. a map
is named after its outstanding cultural or
geographic features.
2. Sheet number – found in the upper right margin and
used as reference number assigned to
each map
3. Series Name and Scale – found on the upper left margin. A
map series usually comprises a group of
smaller maps at some scale designed to
cover a particular geographic area.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
4. Series Number – appears in the upper right margin and
lower left margin.
5. Edition Number – is found in the upper margin and in
the lower margin, representing the age
of the map.
6. Bar Scale – located in the center of the lower margin
and in the lower margin use for
determination of map distance to the
corresponding ground distance with
three different units of measures.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
7. Credit Note – in lower left margin, primary purpose is to list
the procedures and reference, the method
of compilation for used by technicians.
8. Index to Adjoining Sheet – in lower margin, it identifies the
map sheet covering areas around the area
covered by the map you are using.
9. index to boundaries diagrams – in lower margin, this is a
miniature map that shows the boundaries
and special show line that occurs within the
map area.
10. Projection Note – in lower margin, it indicate the method
use to portray the map area.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
11. Grid Note – in the center lower margin, it gives information
pertaining to the grid system used, the initial
guidelines and the number of digit omitted from
grid values.
12. Grid Reference Box - usually located at the center of the
lower margin. it contains information identifying
the grid zone designation and 100,00 meters
square identification.
13. Horizontal Datum Note - located at the center of the lower
margin and defined as geodetic reference
point.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
14. Legend - at the lower left margin, illustrates identifies the
topographic symbols used to depict some of
the prominent features on the map.
15. Declination Diagram - located in he center lower margin
and indicates the relationships of true north and
magnetic north.
16. Protractor Scale – in upper margin, use for laying out a
magnetic north line on the map.
17. User Note – located in the lower margin use for
connections and errors on the map.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
18. Unit Imprint - at the left side of the lower margin, it
identifies the agency which printed the maps
with its respective symbols.
19. Contour Interval Note - located in the center of the lower
margin. it states the vertical distance between
adjacent contour lines on the map. when
supplementary contours are used the interval is
indicated.
20. Coverage Diagram – normally in lower margin, it indicates
the methods by which the map was made,
dates of photography and other sources
material.
MARGINAL INFORMATION
21. Graphic Scale - a ruler used to convert map distance to
ground distance without going through
mathematical computations.
22. Contour Interval – the contour interval states the vertical
distance between adjacent contour lines on the
map. when supplementary contour are used
the intervals is indicated.
23. Vertical Datum Note – it designates the basis for all
vertical control stations, contours and elevation
appearing in the map.
MAP SYMBOL
Purpose:
1.Visualize an area of the earth surface;
2.Represent the natural and man-made feature;
MAP SYMBOL
Classification:
1.Topographic Symbols are standard drawing of
map features and organized by the colors;
MAP SYMBOL
Classification:
1.Topographic Colors:
a) Black- All man-made features; such as buildings,
roads not shown in red, etc
b) Blue- All water features like lakes, rivers, swamps,
streams, etc
c) Brown- All land forms, like contours, cuts, fills, etc
d) Green-All vegetation, such as forest, orchard, jungles,
e) Red- Main roads, built-up areas, and special info
MAP SYMBOLS
TOPOGHAPHIC SYMBOLS
Man-made Objects
MAP SYMBOLS
TOPOGHAPHIC SYMBOLS
Drainage and Vegetation
MAP SYMBOLS
TOPOGHAPHIC SYMBOLS
Drainage and Vegetation
MAP SYMBOLS
MILITARY COLORS
1.Blue- All friendly forces, installations, activities and firepower;
2. Red- All enemy forces, installations, and activities (double lines
means enemy)
3. Yellow- shows grassed or contaminated areas
4. Green-indicates friendly or enemy demolation, minefield and
man-made obstacles
5.Spare Colors-use for classification and accompanied by
legend
MAP SYMBOLS
TYPES OF MILITARY SYMBOLS
1. Troops unit symbols – are shown by rectangle. (basic
symbols for military unit and activities).
2. Branch arm of service and type – organization symbol –
used in conjunction either other symbols to signify
a military unit activity or installation.
3. Size of unit – used to identify the size of a unit or
installation.
GRIDS AND COORDINATES
Grids - are parallel lines from east to west, north or
south that forms a square used as a reference system
to help the map reader locate areas quickly.
Coordinates - are the numbered grid lines on the map
and are further subdivided to show specified location
Geographic Coordinates – the location of any point of
the earth surface maybe given by stating into its
distance north or south of the equator (latitude) and east
or west of prime meridian (longtitude).
GRIDS AND COORDINATES
Polar Coordinates – On The Map Maybe Determined
or plotted from a known point by giving a distance along
that direction.
Grid Coordinates - the military grid system divides the
earth surface into many 100,000 meter squares. each of
these squares are further subdivided into 1,000 meter
squares. the 1,000 meter squares is the basis of the
military grid system which is used in reading military
map.
GRIDS AND COORDINATES
Grid Square - can be located or identified by combining
the number of the vertical grid line and horizontal grid
line which intersect at the lower left corner of the
square.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GRIDS
Does not requires knowledge of the area
Applied to large areas
Does not requires land marks
Applies to all map scales
GRAPHIC (BAR) SCALE
Is the most accurate means of measuring distance on a
map.
It is the ruler printed on the map which distances on the
map may be measured as actual ground distance;
GRAPHIC (BAR) SCALE
Two parts of Graphic (Bar) Scale:
LOCATING PT OF GRID SQUARE
TERRAIN FEATURES
Five Major: Hidden Valley Ranch Salad Dressing Hilltop,
Valley, Ridge, Saddle, Depression
Three Minor: Draw, Spur, Cliff
Two Supplementary: Cut, Fill
TERRAIN FEATURES
Hill- An area of high ground. When you are located on
a hilltop, the ground slope down in all directions;
TERRAIN FEATURES
Valley- A stretched-out groove in the land, usually formed
by streams or rivers
TERRAIN FEATURES
Ridge- A sloping line of high ground
TERRAIN FEATURES
Saddle- A deep or low point between two areas of higher
ground between two hilltops
TERRAIN FEATURES
Depression- Low point in the ground or sinkhole. they are
represented by close contour lines that have
tick marks pointing toward low ground
TERRAIN FEATURES
Draw- a less developed steam course than a valley. there
is essentially no level ground and, therefore, little
or no maneuver room within its confines
TERRAIN FEATURES
Spur- a short, continuous sloping line of higher ground,
normally jutting out from the side of a ridge
TERRAIN FEATURES
Cliff- a vertical or near vertical feature; it is an abrupt change of
the land. the slope is so steep that the contour lines
converge into one contour line or the last contour line has
tick marks pointing to low ground
TERRAIN FEATURES
Cut- man-made feature resulting from cutting through raised ground,
usually to from a level bed for a road or railroad track;
Fill- man-made feature resulting from filling a low area, usually to form
a level bed for a road or rail- road track
ELEVATION IN METERS
Three types of contour lines:
1. Intermediate: are contour lines located between two index
lines.
2. Supplementary: are contour lines placed to specify half of the
contour interval. Example: contour interval 20
meters 100m 120m 130m and 140m
3. Supplementary contours 10 meters index: are major elevation
points and have the elevation number written
within the contour. (Ex.100m,200m,300m)
FINDING POINTS
1. Orient the map: Compass or Terrain Association
2. Compass Technique: Cheek and Center hold
methods
3. Grid Coordinates: Grid Zone Designator (RP) and
number sequence (four digit, six digit or eight digit)
4. Remember: READ right then up
5. Dead Reckoning
FINDING POINTS
Parts of Lensatic Compass
FINDING POINTS
Parts of Lensatic Compass
FINDING POINTS
Compass Technique
Compass to cheek method center
hold method the compass to
cheek technique is used almost
exclusively for sighting and is the
best technique for this purpose.
the center hold method is much
faster but is also less precise.
FINDING POINTS
Orienting the Map
A map is oriented
when it is in a horizontal
position with its north/
south corresponding to
the north/ south on the
ground
FINDING POINTS
Military protractor
FINDING POINTS
Grid Coordinates
FINDING POINTS
Grid Precision
FINDING POINTS
Grid Precision
TOPOGHAPHIC SYMBOLS
Man-made Objects
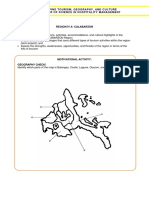
TERRAIN IDENTIFICATION TEST
Stations:
1. Shoot two azimuths, either in MILS or DEGS using
both methods;
2. Given a known point ID its 4-Digit or • 8-Digit
coordinate;
3. a) Find Pace Count.
b) Given a 4 digit and an 8 digit coordinate • plot
both points and ID the Feature or structure
End of presentation!!!