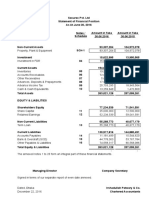
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
• FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIZING
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DEFINITION AND PURPOSES
• Organizing is the process of assigning tasks, allocating
resources and coordi-nating work activities.
• Organizing is the process of arranging people and other
resources to work together to accomplish a goal.
• It identifies who is to do what, who is in charge of whom,
and how different people and parts of the organization
relate to and work with one another ---- Structure & Chart
71
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE AND
CHART (FORMAL STRUCTURE)
• ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE is a system of tasks,
reporting relationships and communication channels that
links together the work of diverse individuals and groups
• ORGANIZATION CHART is a diagram that describes the
arrangement of work positions through lines of authority
and communication within an organization
72
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
LEARN FROM AN
ORGANIZATION CHART
• Division of Work : Positions and titles show work responsibilities
• Supervisory Relationships : Lines show who reports to whom
• Communication Channels : Lines show formal communication
flows
• Major Subunits : Positions reporting to a common manager are
shown
• Levels of Management : Vertical layers of management are shown.
73
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
INFORMAL STRUCTURE WITHIN
ORGANIZATION
• INFORMAL STRUCTURE is the set of unofficial
relationships among an organiza-tion’s members.
• Behind every formal structure typically lies an informal
structure. This is a ‘shadow’ organization made up of the
unofficial, but often critical, working relationships between
organizational members
74
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ADVANTAGES OF INFORMAL
STRUCTURE
• Helpful in getting work accomplished
• The emergent and spontaneous relationships in formal
structure so that they make contacts with others who can
help them get things done when necessary.
• Helpful in giving people access to emotional support &
friendship that satisfy important social needs
75
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DISADVANTAGES OF INFORMAL
STRUCTURE
• Because they exist outside the formal authority system,
informal structures can sometimes work against the best
interests of the organization as a whole.
• They can be susceptible to rumor
• They can carry inaccurate information
• They can breed resistance to change and even divert work
efforts from important objectives.
76
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
GLOSSARY IN ORGANIZATION
STRUCTURE
• LINE MANAGERS are responsible for the essential activities
of the organization, including production and sales. Line
managers have the authority to issue orders to those in the chain
of command
• STAFF MANAGERS have advisory authority, and cannot issue
orders to those in the chain of command (except those in their
own department)
• SPAN OF CONTROL is the number of employees who can be
effectively and efficiently supervised by a manager
77
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
GLOSSARY IN ORGANIZATION
STRUCTURE
• AUTHORITY is The rights inherent in a managerial position to
tell people what to do and to expect them to do it
• CENTRALIZATION is the degree to which decision making is
concentrated at a single point in the organization
• DECENTRALIZATION is the degree to which lower-level
employees provide input or actually autonomy to make decisions
• FORMALIZATION is the degree to which jobs within the
organization are standardized and the extent to which employee
behavior is guided by rules and procedures
78
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
APPROACHES
• TRADITIONAL / CONVENTIONAL APPROACHES
• a. Functional Structure
• b. Divisional Structure
• c. Matrix Structure
• NEWER / CONTEMPORARY APPROACHES
• a. Team Structure
• b. Network Structure
• c. Boundaryless Organization Structure
79
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
TRADITIONAL / CONVENTIONAL
APPROACHES
• Functional Structure
• Divisional Structure
• Matrix Structure
80
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE
• is a structure that people with similar skills and performing
similar tasks are grouped together into formal work units.
• Members of functional departments share technical
expertise, interests & responsibilities.
• This structure common in business firms, with top
management arranged by the functions of marketing,
finance, production, human resource, etc.
81
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE
CHART
DIRECTOR
Manager, Manager, Manager, Manager, Manager,
Engineering Accounting Manufacturing Human Resources Purchasing
+Efficiencies from putting together similar specialties and people with common
skills, knowledge, and orientations
+ Coordination within functional area
+ In-depth specialization
– Poor communication across functional areas
– Limited view of organizational goals
82
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL
STRUCTURE
• Economies of scale with efficient use of resources
• Task assignments consistent with expertise and training
• High-quality technical problem solving
• In-depth training and skill development within functions
• Clear career paths within functions.
83
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DISADVANTAGES OF
FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE
• Difficult in pinpointing responsible for things like cost
containment, product or service quality, timeliness and
innovation in response to environment changes.
• Such problems with functional structures become magnified as
organizations grow in size and environments begin to change
• Lack of communication , coordination and problem solving
Because the functions become formalized not only on an
organization chart but also in the mindsets of people, the sense
of coopera-tion and common purpose breaks down
84
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE
• is a structure that group of peoples work on the same product or
process, serve similar customers, and/or are located in the same
area or geographical region.
• The types of Divisional Structure:
• 1. By Product / Market Structure
• 2. By Customer Structure
• 3. By Geographical Structure
• 4. By Process Structure
85
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DIVISION STRUCTURE BY
PRODUCT/MARKET: AN EXAMPLE CHART
Manufacturing
Director
Shoes and Sandal Clothes Toileteries Skin Care
Division Manager Division Manager Division Manager, Division Manager,
86
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DIVISION STRUCTURE BY
CUSTOMER: AN EXAMPLE CHART
Manufacturing
Director
Male Shoes Female Clothes Children Toys Adult Magazine
Division Manager Division Manager Division Manager, Division Manager,
87
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DIVISION STRUCTURE BY
GEOGRAPHICAL: AN EXAMPLE CHART
Manufacturing
Director
East-Java West-Java Bali Sumatra
Division Manager Division Manager Division Manager, Division Manager,
88
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DIVISION STRUCTURE BY
PROCESS: AN EXAMPLE CHART
Manufacturing
Director
Clothes Design Cutting Sewing Packaging
Division Manager Division Manager Division Manager, Division Manager,
89
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ADVANTAGES OF DIVISIONAL
STRUCTURE
• More flexibility in responding to environmen-tal changes
• Improved coordination across functional department
• Clear point of responsibility for product or service delivery
• Expertise focused on specific customers, products and
regions
• 5. Greater ease in changing size by adding or deleting
divisions
90
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DISADVANTAGES OF
DIVISIONAL STRUCTURE
• Reduce economies of scale
• Increase costs through the duplication of resource and
efforts across divisions
• Create unhealthy rivalries as divisions compete for
resources and top management attention and as they
emphasize division needs and goals to the detriment of the
goals of the organi-zation as a whole
91
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
MATRIX STRUCTURE
• is combines functional and divisional approaches to
emphasize project or program team.
• In effect, it is an attempt to gain the advan-tages and
minimize the disadvantages of each
• This is accomplished by using the permane-nt cross-
functional teams to support specific products, projects or
programs.
•
92
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
ADVANTAGES OF MATRIX
STRUCTURE
• Better cooperation across functions
• Increased flexibility in adding, removing and/or changing operations to meet
changing demands.
• Better customer service, since there is always a program, product or project manager
informed and available to answer questions
• Better performance accountability through the program, product or project managers
• Improved decision making as problem solving takes place at the team level, where
the best information is available
• Improved strategic management, since to managers are freed from unnecessary
problem solving to focus time on strategic issues
93
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
DISADVANTAGES OF MATRIX
STRUCTURE
• The two-boss system is susceptible to power struggles. It
can create task confu-sion and conflicts in work priorities.
• Time consuming
• Teams may develop “groupthink” or strong team loyalties
that cause a loss of focus on larger organizational goals.
• The requirements of adding the team leaders to a matrix
structure can result in increased costs
94
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
NEWER / CONTEMPORARY
APPROACHES
• TEAM STRUCTURE
• NETWORK STRUCTURE
• BOUNDARYLESS ORGANI-ZATION
• REMOVING ORGANIZA-TION
95
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
TEAM STRUCTURE
• Uses permanent and temporary cross functional teams to improve lateral relations
and solve problems throughout an organization. Team structure involves :
• A Cross-Functional Team ; brings together
• members from different functional departments
•
• b. Project Teams ; are convened for a particular
• task or project and disband once it is completed
•
96
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
NETWORK STRUCTURE
• A small core organization that outsources its major business functions
(e.g., manufacturing) in order to concen-trate on what it does best
• This structure is uses IT to link with networks of outside suppliers
and service contractors
97
LABORATORIUM MSDM, PENGANTAR MANAJEMEN
BOUNDARYLESS ORGANIZATION
• A flexible and an unstructured organization-al design that is
intended to break down external barriers between the
organization and its customers and suppliers
• Removes internal (horizontal) boundaries:
• Eliminates the chain of command
• Has limitless spans of control
• Uses empowered teams rather than departments
• Eliminates external boundaries:
• Uses virtual, network, and modular organizati-onal structures to
get closer to stakeholders
98