LATHE MACHINE
GROUP 1
LATHE MACHINE
LATHE MACHINE
Is amachine toolthat rotates the
workpiece on itsaxisto perform various
operations such
ascutting,sanding,knurling,drilling,
ordeformation,facing,turning, with
tools that are applied to the workpiece
to create an object with
symmetryabout anaxis of rotation.
LATHE MACHINE
Are used
inwoodturning,metalworking,metal
spinning,thermal spraying, parts
reclamation, and glass-working. Lathes
can be used to shapepottery, the best-
known design being thepotter's wheel.
Most suitably equipped metalworking
lathes can also be used to produce
mostsolids of revolution, plane surfaces
and screw threads orhelices.
TYPES OF A
LATHE MACHINE
CENTER LATHE
Most frequently used lathe
Heavy duty
power drive for most tool movements
Size range 12x24 to 24x48 - can be larger
BENCH LATHE
A bench top model usually of low power
used to make precision machine small work pieces
TOOL ROOM LATHE
Look like engine lathe
Greater accuracy
More versatility
Wider range of speeds and
feeds
TURRET LATHE
- Capable of performing multiple cutting
operations on the same workpiece (Turning,
Boring, Drilling, Thread cutting, Facing)
Turret Head
- Turret lathes are very versatile
CAPSTAN LATHE
It is production lathe
Used for light duty
work pieces Turret Head
Small in size as
compared to turret
lathe
It also have turret
that replaces
tailstock
Multiple tools set to
machine part
Still may require
some operator skill
TRACER/COPY LATHE
Hydraulic attachment used to copy the shape of a part
from a master.
lathe that has the ability to follow a template to copy
a shape or contour.
Machine tools with attachments
Capable of turning parts with various contours
A tracer finger follows the template and guides the
cutting tool
Tracer piece
AUTOMATIC LATHE
An automatic lathe is
a lathe (usually a
metalworking lathe)
whose actions are
controlled
automatically. Although
all electronically
controlled (CNC) lathes
are automatic, they are
usually not called by
that name, as
explained under
"General
nomenclature". The
CNC LATHE
Computer controlled
Wide variety of
Machine Unit NC controller
process capability
multiple axis
Indexing and
contouring head
On- line and off- line
programming
available
Computer Numerical
Controls (CNC)
Equipped with one or
more turrets
Each turret is
equipped with a
variety of tools
Performs several
operations on
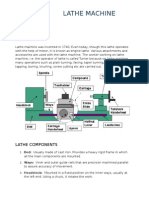
PARTS OF A LATHE MACHINE
Spindle Tailstock
Nose Tool Post Spindle
HEADSTOCK Compound Clamp TAILSTOCK
Rest
Saddle
Feed
Change
Lever
Feed Lead
BED
Reverse Screw
WAYS
Lever
APRON
Bed
Gear Friction- Half Nut
Carriage
Box clutch Lever
Hand
Wheel Control
Motor Cross
Drive Slide
LATHE BED
Heavy, rugged casting
Made to support working parts of lathe
On top section are machined ways
Guide and align major parts of lathe
15
LATHE BED
16
HEADSTOCK
Clamped on left-hand end of bed
Headstock spindle
Hollow cylindrical shaft supported by
bearings
Provides drive through gears to work-
holding devices
Live center, faceplate, or chuck fitted
to spindle nose to hold and drive work
Driven by stepped pulley or
transmission gears
Feed reverse lever
Reverses rotation of feed rod and lead
screw
17
HEADSTOCK
18
QUICK-CHANGE GEARBOX
Contains number of different-size
gears
Provides feed rod and lead-screw
with various speeds for turning and
thread-cutting operations
Feed rod advances carriage when
automatic feed lever engaged
Lead screw advances the carriage for
thread-cutting operations when split-
nut lever engaged 19
QUICK-CHANGE GEARBOX
Top View 20
CARRIAGE
Used to move cutting tool along
lathe bed
Consists of three main parts
Saddle
H-shaped casting mounted on top of
lathe ways, provides means of mounting
cross-slide and apron
Cross-slide
Apron
21
CARRIAGE
22
CARRIAGE
23
CROSS-SLIDE
Mounted on top of saddle
Provides manual or automatic cross
movement for cutting tool
Compound rest (fitted on top of cross-
slide)
Used to support cutting tool
Swiveled to any angle for taper-turning
Has graduated collar that ensure accurate
cutting-tool settings (.001 in.) (also cross-
slide)
24
CROSS-SLIDE
25
APRON
Fastened to saddle
Houses gears and mechanism required
to move carriage or cross-slide
automatically
Locking-off lever inside apron prevents
engaging split-nut lever and automatic
feed lever at same time
Apron handwheel turned manually to
move carriage along lathe bed
26
APRON
27
AUTOMATIC FEED LEVER
Engages clutch that provides
automatic feed to carriage
Feed-change lever can be set for
longitudinal feed or for crossfeed
In neutral position, permits split-nut lever
to be engaged for thread cutting
Carriage moved automatically when split-
nut lever engaged
28
TAILSTOCK
Upper and lower tailstock castings
Adjusted for taper or parallel turning by
two screws set in base
Tailstock clamp locks tailstock in any
position along bed of lathe
Tailstock spindle has internal taper to
receive dead center
Provides support for right-hand end of work
29
TAILSTOCK
30
LATHE OPERATIONS
Turning: produce straight, conical, curved, or grooved
work pieces
Facing: to produce a flat surface at the end of the part or
for making face grooves.
Boring: to enlarge a hole or cylindrical cavity made by a
previous process or to produce circular internal grooves.
Drilling: to produce a hole by fixing a drill in the tailstock
Threading: to produce external or internal threads
Knurling: to produce a regularly shaped roughness on
cylindrical surfaces
LATHE OPERATIONS
32
STANDARD OPERATING
PROCEDURE
1. Ensure the main power is turned off when
doing Total Preventive Maintenance.
2. Know where the emergency stop button is
located on your machine before operating.
3. Practice good house keeping, return tools to
the proper location after use.
4. Try to eliminate long, stringy chips when
machining as they can be easily caught up in
the chuck and cause personal injury, always
exercise proper chip control.
5. Know machine speeds and feeds, if you are
unsure please ask your supervisor.
STANDARD OPERATING
PROCEDURE
6. Make sure cutting tools are used properly and for their
intended application.
7. Do not try and fix the machine if there is a problem,
ask your supervisor to contact plant maintenance.
8. Ensure that auto stops are set before starting a job.
Make sure cutting tools are centered and securely
fastened.
9. Ensure the lathe you operate and tooling is used with
respect at all times.
10. Never use compressed air to clean the lathe, as small
particles may become embedded into parts of the
machine causing damage, use a soft bristle brush.
11. Never leave a running (spindle turning) lathe
unattended.