What is Computer Memory?
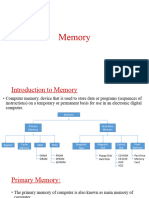
A physical device that stores data or information temporarily or permanently in it is called memory. Its a
device where data is stored and processed. In common, a computer has primary and secondary
memories. Auxiliary (secondary) memory stores data and programs for long-term storage or until the
time a user wants to keep them in memory, while main memory stores instructions and data during
programme execution;
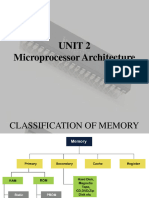
Types of Computer Memory
Computer memory comes in various types and serves different purposes −
Primary Memory (RAM - Random Access Memory) − Volatile memory loses its contents when the
machine is turned off. RAM stores the data that is actively being used. During the booting process of a
system, the operating system actively uses RAM and applications that are necessary to execute a file or
a program. It speeds up CPU processing by providing fast data and instruction access.
Secondary Memory (Storage) − Secondary Memory is also known as permanent memory or non-volatile
memory of a computer. Secondary memory retains data when the machine shuts down. Files,
programmes, and the OS are stored there permanently. HDDs, SSDs, USB flash drives, and optical discs
are non-volatile memory devices.
Cache Memory − Memory that is smaller and faster than RAM is called cache memory. It is placed closer
to the CPU than the RAM. It saves data and instructions that are used a lot so that processing goes
faster.
Register Memory − Register memory, which is also called processor registers or "registers," is the
smallest and fastest type of computer memory that is directly integrated into the CPU. Registers are
small, fast storage units inside the CPU that are used to quickly store data that is being processed or
instructions that are being run.
Primary Memory
Computer primary memory is also known as volatile memory, as it loses contents when the machine is
turned off. There are two types of primary memory: RAM and ROM. RAM stores the data that is actively
being used. During the booting process of a system, the operating system actively uses RAM and
applications that are necessary to execute a file or a program. It speeds up CPU processing by providing
rapid data and instruction access.
Here is the classification of primary memory:
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
2. SRAM (Static RAM)
3. DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
4. SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)
5. DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM
6. ROM (Read-Only Memory)
7. PROM (Programmable ROM)
8. EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM)
1. Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM contains of a various number of memory locations wherein each location, typically 8-bits
are stored. It can be possible to read from a RAM location, as well as write to a RAM location.
The drawback of RAM is that it is volatile.
2. Read Only Memory (ROM)
ROM consists of a number of memory locations wherein each location typically stores 8 bits like
a RAM. A ROM also uses random access method just like a RAM. The advantage of ROM is that it
is non-volatile in nature. That means, though the power supply to the ROM is switched off, the
information in the ROM will not be lost
3. Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM) The user writes information to this type of ROM
using a PROM programmer. Once written, the information cannot be changed. Like Mask-
Programmed ROM, the information is permanent. It is more expensive than mask ROM but
allows purchasing in smaller quantities.
4. Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM) Information is written by the user with
an EPROM programmer. As its content is erasable and rewritable, the user can modify it
multiple times. Data is erased using strong ultraviolet (UV) light on the quartz window of the
EPROM chip, which removes all content. Users can purchase a single piece of EPROM and
rewrite its content multiple times.
5. Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM) Information is written by
the user using an EPROM programmer. Unlike EPROM, EEPROM data is erased using electrical
signals rather than UV light. EEPROM allows selective data erasure and is more expensive than
other ROM types. It is gaining popularity due to its flexibility.
Secondary Memory
Computer secondary memory stores data and programs permanently, even when the computer
is off.The secondary memory is also known as external memory or auxiliary memory.
Classification of Secondary Memory
Here is the complete classification of secondary memory:
1. Magnetic Storage
2. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
3. Floppy Disk (Obsolete)
4. Magnetic Tape
5. Optical Storage
6. CD (Compact Disc)
7. CD-ROM (Read-Only Memory)
8. CD-R (Recordable)
9. CD-RW (Rewritable)
10. DVD (Digital Versatile Disc)
11. DVD-ROM
12. DVD-R/DVD+R
13. DVD-RW/DVD+RW
14. Blu-ray Disc (BD)
15. Flash Storage (Solid-State Storage)
16. Solid-State Drive (SSD)
17. USB Flash Drive (Pen Drive)
18. Memory Cards (SD Card, microSD, etc.)
19. Cloud Storage
20. Google Drive
21. Dropbox
22. OneDrive
23. Amazon S3
24. Hybrid Storage
25. Hybrid Drive (HDD + SSD Combination)
26. SSHD (Solid-State Hybrid Drive)
27. Cache Memory
Cache memory is smaller and faster than RAM. It is placed closer to the CPU than the RAM.
Cache
Different types of cache memory, like L1, L2, and L3 cache, have different speeds and amounts
of space.
The Levels of Cache Memory: L1, L2, and L3