Republic of the Philippines
BATANGAS STATE UNIVERSITY
The National Engineering University
Alangilan Campus
Golden Country Homes, Alangilan Batangas City, Batangas, Philippines 4200
Tel Nos.: (+63 43) 425-0139 local 2121 / 2144
E-mail Address:
[email protected] | Website Address: http://www.batstate-u.edu.ph
College of Engineering – Department of Civil Engineering
QUIZ NO. 1
CE 420 – CE Practice with Comprehensive Examination
Second Semester, AY 2024 –2025
GENERAL DIRECTION: Shade the letter of your answer on the answer
sheet provided. Use pencil if necessary for shading.
I. GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
SITUATION 1: Answer the following terms for the geotechnical
engineering.
1. The shear strength of a soil at liquid limit is
a. zero b. very small
c. high d. hard to determine
2. If the soil on the top of the clay is sand and the layer below
the clay is impervious, determine the amount of time required for
50% of the total settlement to occur.
a. 18 to 19 years b. More than 19 years
c. Less than a year d. More than 5 years
3. For large engineering projects, the permeability is determined
by:
a. constant head test b. pumping in test
c. falling head test d. pumping out test
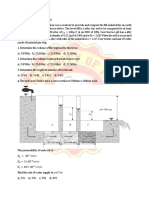
SITUATION 2: A tank shown in the figure has an inside diameter of
8 m and a height of 6 m. It is used as storage of oil with specific
gravity of 0.80. The combined weight of the empty tank and the
footing is 2,800 kN.
4. Which of the following most nearly gives the required depth of
the footing?
a. 2.99 m b. 2.38 m
c. 2.71 m d. 2.53 m
5. Which of the following most nearly gives the increase in
pressure in the soil when the tank is filled with oil?
a. 43.16 kPa b. 59.48 kPa
c. 55.27 kPa d. 47.09 kPa
6. Which of the following most nearly gives the settlement of the
clay layer? Assume that the swell index is equal to one-fifth of
the compression index.
a. 96.23 mm b. 90.35 mm
c. 78.57 mm d. 72.75 mm
SITUATION 3: A direct shear test was conducted on a specimen of
dry sand with a normal stress of 191.50 kPa. Failure occurred at
a shear stress of 119.70 kPa. The size of the sample tested was
50.8 mm x 50.8 mm x 25.4 mm.
7. Which of the following most nearly gives the angle of friction?
a. 32.01 b. 13.34
c. 38.69 d. 23.81
8. Which of the following most nearly gives the angle of failure
plane?
a. 64.35 b. 61.01
c. 56.91 d. 51.67
9. For a normal stress of 144 kPa, which of the following most
nearly gives the required shear force to cause failure in the
sample?
a. 163.98 N b. 297.61 N
c. 232.30 N d. 88.12 N
SITUATION 4: A braced cut in sand 10 m deep is shown below. In
the plan, the struts are spaced center-to-center at 4m. Use
apparent pressure distribution diagrams as proposed by Peck.
10. Which of the following most nearly gives the load on strut A?
a. 314.35 kN b. 163.46 kN
c. 78.59 kN d. 408.65 kN
11. Which of the following most nearly gives the load on strut C?
a. 314.35 kN b. 163.46 kN
c. 78.59 kN d. 408.65 kN
12. Which of the following most nearly gives the load on strut B?
a. 62.87 kN b. 326.92 kN
c. 163.46 kN d. 502.95 kN
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation
SITUATION 5: In a specific gravity test, the following data are
collected:
Weight of saturated oven-dried soil = 2.05 N
Weight of soil + partial water + pyconometer = 6.75 N
Weight of pycnometer full of water = 5.97 N
The acceleration due to gravity is assumed to be 9.81 m/s2.
13. Calculate the specific gravity of soil solids if the density
of the water at the temperature of the test is 997 kg/m3.
a. 2.91 b. 1.16
c. 2.19 d. 1.61
14. Accidentally, 2.2 cm3 of air got entrapped while determining
the weight of pycnometer, soil and partial water. What is the
correct value of the specific gravity? The density of the water at
the temperature of the test is 997 kg/m3
a. 1.64 b. 2.94
c. 1.46 d. 2.49
15. Which of the following most nearly gives the percentage error
in determining the specific gravity due to the entrapped air?
a. 1.03% b. 1.14%
c. 1.67% d. 1.72%
SITUATION 6: The soil formation shown below has a constant width
of 35 cm perpendicular to the figure. The respective hydraulic
conductivities are 1) 28.8 mm/hr, 2) 187.2 mm/hr, 3) 21.6 mm/hr,
4) 36 mm/hr and 5) 3.6 mm/hr. The thickness of the layers are h1
= h4 = 350 mm and h2 = h5 = 900 mm. The head difference (H) is
1250 mm. The horizontal measurements are x1 = 430 mm, x2 = 320 mm
and x3 = 400 mm.
16. Determine the equivalent hydraulic conductivity of the soil
formation.
a. 63.8 mm/hr b. 24.8 mm/hr
c. 42.7 mm/hr d. 23.3 mm/hr
17. Calculate the hydraulic gradient of the flow.
a. 1.067 b. 1.087
c. 1.000 d. 0.920
18. Calculate the rate of flow through the soil.
a. 10.8 L/hr b. 11.8 L/hr
c. 11.1 L/hr d. 20.3 L/hr
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation
SITUATION 7: The phase diagram of a soil sample is shown below:
The soil sample is in a container with constant cross-sectional
area of 4000 mm2. The total height (h1 + h2) of the container is
200 mm.
19. If the voids is full of 300 g of water, calculate the ratio
of h1 and h2.
a. 0.60 b. 0.75
c. 0.20 d. 0.45
20. Given that h1 = 68 mm and the soil is 50% saturated, calculate
the weight of the soil sample. The specific gravity of the soil
solids is 2.72.
a. 16.95 N b. 21.04 N
c. 16.76 N d. 15.42 N
21. If the total mass of the soil sample in saturated condition is
1520 g, calculate its porosity. The specific gravity of the soil
solids is 2.65.
a. 55% b. 31%
c. 45% d. 35%
SITUATION 8: A cut slope was excavated in saturated clay as shown
in figure. The soil has a unit weight of 17 kN/m3and an undrained
shear strength cu = 20 kPa. The slope makes an angle of 60degrees
with the horizontal. Assume stability number m = 0.185. Slope
occurs along the plane AC with BC = 8m.
22.Which of the following most nearly gives the stability factor?
a. 5.41 b. 6.50
c. 5.92 d. 6.31
23.Which of the following most nearly gives the maximum depth up
to which the cut could be made?
a. 5.99 m b. 7.21 m
c. 6.82 m d. 6.36 m
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation
24.Which of the following most nearly gives the angle that the
failure plane makes with the horizontal?
a. 28.58 b. 29.74
c. 30.65 d. 27.60
25. Soils are permeable due to the existence of:
a. fines b. interconnected voids
c. voids d. large particles
26. Boussinesq (1883) solved the problem of stresses produced at
any point as a result of a point load on the surface of infinitely
large half-space in
a. homogeneous medium b. elastic medium
c. isotropic medium d. all of the above
SITUATION 9: The figure shows a layer of granular soil in a tank
where upward seepage of water is caused by opening the value
located below the tank. The rate of water supply is kept constant.
Assume the soil has reached boiling (zero effective stress).
27. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical hydraulic
gradient?
a. 1.15 b. 1.52
c. 2.15 d. 2.51
28. Which of the following most nearly gives the elevation of water
in the piezometer placed at point A?
a. 7.28 m b. 8.03 m
c. 7.6 m d. 7.85
29. Which of the following most nearly gives the elevation of water
in the piezometer placed at point B if the elevation of point B is
1 m?
a. 6.43 m b. 6.54 m
c. 6.88 m d. 6.97 m
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation
SITUATION 10: A pile group consisting of 9 piles, each 0.40 m in
diameter, is arranged in a 3 × 3 matrix at a spacing of 1.20 m.
The piles penetrate a soft clay (c = 20 kPa, = 30°, y = 17 kN/m')
of thickness 8 m and are embedded 2 m in a stiff clay (c = 90 kPa,
ф = 28°, y = 17.5 kN/m3). Use a = 1 for soft clay and α = 0.50 for
stiff clay. Nc = 9.
30. Which of the following most nearly gives the capacity of the
pile group based on single pile failure mode?
a. 3,743.55 kN b. 3,646.98 kN
c. 3,432.24 kN d. 3,826.17 kN
31. Which of the following most nearly gives the capacity of the
pile group based on block failure mode?
a. 9,150.40 kN b. 10,167.49 kN
c. 8,732.91 kN d. 9,733.10 kN
32. Which of the following most nearly gives the center-to-center
spacing of the piles for an efficiency factor of 1?
a. 0.72 m b. 0.61 m
c. 0.55 m d. 0.68 m
33. For the flow of water through the void spaces of most saturated
soils,
a. discharge velocity is proportional to the square of
hydraulic gradient.
b. discharge velocity is proportional to the hydraulic
gradient.
c. discharge velocity is inversely proportional to the
hydraulic gradient.
d. discharge velocity is inversely proportional to the square
of hydraulic gradient
SITUATION 11: A retaining wall 12 m high has a horizontal ba water
content of 12 Face to its base. Under normal conditions, the
backfill has a water content of 12% and a void ratio of 0.45. The
specific gravity of the soil grains is 2.65 and the angle of
internal friction is 20°. When the backfill is fully saturated
with rain water:
34. Evaluate the total horizontal lateral force per meter width
of wall, in kN, due to the water.
a. 706 b. 652
c. 563 d. 825
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation
35. Evaluate the total horizontal lateral force per meter width of
wall, in kN, due to the soil.
a. 426 b. 394
c. 352 d. 240
36. How many times would the horizontal lateral force be increased
if the backfill is fully saturated with rain water compared to its
normal condition?
a. 1.55 b. 1.65
c. 1.36 d. 1.06
37. Which component of rock or soil is independent of interparticle
friction?
a. adhesion b. plasticity
c. cohesion d. skin friction
SITUATION 11: A soil profile consists of dry sand and clay being
the latter as the bottom layer. The ground water table is initially
located at the interface of the two soils. The sand has e = 0.65,
G = 2.66 and H = 3 m while the clay has e = 0.90, G = 2.75, H = 11
m, LI = 42.4% and PL = 20%.
38. Determine the compression index.
a. 0.43
b. 0.36
c. 0.51
d. 0.22
39. Determine the effective stress increase with the water
table lowered by 5 m.
a. 25.8 kPa
b. 63.9 kPa
c. 93.3 kPa
d. 30.7 kPa
40. Determine the settlement.
a. 248.8 mm
b. 457.8 mm
c. 409.6 mm
d. 213.4 mm
*** END ***
WARNING: Failure to submit your Test Questions (Complete) set
will cause the cancellation of your Test Results for
the subject.
Leading Innovations, Transforming Lives, Building the Nation