0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views10 pagesInterrupts in 8051 Microcontroller
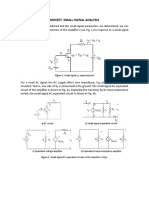
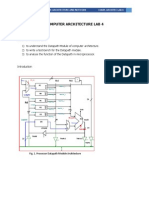
The document provides an overview of interrupts in the 8051 microcontroller, explaining their purpose, types, and execution process. It details various interrupt sources, the interrupt enable (IE) and interrupt priority (IP) registers, and includes an example of using an external interrupt to control an LED. Additionally, it discusses applications of interrupts for timers, serial communication, and external events.
Uploaded by
Gaurav BhaisareCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
259 views10 pagesInterrupts in 8051 Microcontroller
The document provides an overview of interrupts in the 8051 microcontroller, explaining their purpose, types, and execution process. It details various interrupt sources, the interrupt enable (IE) and interrupt priority (IP) registers, and includes an example of using an external interrupt to control an LED. Additionally, it discusses applications of interrupts for timers, serial communication, and external events.
Uploaded by
Gaurav BhaisareCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10