0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesUnderstanding Sampling Gates in Circuits
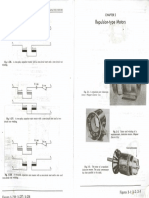
Sampling gates select transmission signals during specific time intervals, producing an output that matches the input or is zero otherwise. They can be unidirectional or bidirectional, constructed using diodes or BJTs, and utilize series or shunt switches to determine the transmission and non-transmission periods. Unlike digital logic gates, sampling gates are analog and provide an exact replica of the input signal during the transmission period.
Uploaded by
Ramesh BoseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views2 pagesUnderstanding Sampling Gates in Circuits
Sampling gates select transmission signals during specific time intervals, producing an output that matches the input or is zero otherwise. They can be unidirectional or bidirectional, constructed using diodes or BJTs, and utilize series or shunt switches to determine the transmission and non-transmission periods. Unlike digital logic gates, sampling gates are analog and provide an exact replica of the input signal during the transmission period.
Uploaded by
Ramesh BoseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2