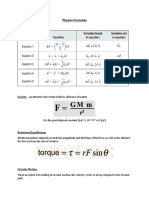
General Physics
Quantity Formula Explanation S.I UNIT Definition
Cm3 or m3
The Size of a
Volume Length x breath x height
particular shape is
called its volume
The mass per unit
Density=mass/volume When mass and
Density Kg/m3 or g/cm3 volume of a
D =m/v volume is given
substance is called
its Density
m/s
The rate of change
Speed= distance/time When distance
Speed km/h of distance is called
v = d/t and time is given
speed
The rate of change
Acceleration=speed/time When speed and 2 2 of velocity is called
Acceleration m/s or km /h
a = v/t time is given acceleration
1) Vav = V + U m/s
2
m/s
Equations of
2) V = U + at
motion
3) S = ut + ½ at m
4) 2as = V2-U2
m2/s2
When mass and A push or a pull of an
F=mass x acceleration Newton (N) or kg x object is called force
Force acceleration is
F= m . a m/s2
given
When object is The force of
Weight= mass x acceleration
moving toward or Newton (N) or attraction from the
Weight due to gravity
away from kg x m/s2 gravity is called
W= m .g
gravitational field weight
Moment of Moment of force = force x When force and N.m
force perpendicular distance form perpendicular The turning effect of
pivot distance form force about a fixed
pivot is given point(pivot) is called
M= F X d moment
Momentum =mass x velocity
Momentum Kg . m/s
Impulse = force x time
Impulse N.s
Quantity Formula S.I UNIT
Force = spring constant x
Extension With in elastic limit
Newton extension is directly
Elastic force
(N) proportional to force
F=kx
F X X
Pressure= force/area Pascal (pa)
The force per unit
Pressure
Area of an object is
P = F /A N/m2
called its pressure
Density of liquid is ρ
When density
in kg/m3, h is height
Pressure= density x gravitational gravity
Pressure in Pascal (pa) or depth of liquid in
acceleration x depth acceleration
liquid N/m2 meter and g is
P=ρ.g.h and depth is
acceleration due to
given
gravity (10m/s2)
Efficiency = useful energy
output x 100%
Useful energy input
Efficiency No unit
Efficiency = work done by the
machine x 100%
Work done on the machine
Kinetic Energy K.E = ½ mass x velocity2 When mass
and velocity is joules Energy due to the
2
K.E = ½ m v given motion of an object
is called its Kinetic
energy
Potential Energy When mass
P.E = mass x gravitational gravitational joules Energy due to the
acceleration x height acceleration height of an object
and height is from earth is called
P.E = m .g. h given its G.P.E
W = force x distance Joules
Work Done F is the Force and d
W = F . d (horizontal) is distance covered
by the object in the
W = m.g.h (vertical) direction of force
Power = work done Watts
Power Time taken Power is the rate of
(mechanical) Joules/sec doing work or rate of
P = w/t transferring the
energy from one
P = F. V form to other
THERMAL PHYSICS
BOYLES LAW P1 . V1 = P2 . V2 At constant
3
V 1 = P2 . V2 m temperature and
P1 Pascal mass the volume of
VOLUME P 1 = P2 . V2 given gas is
V1 proportional to its
pressure
PRESSURE
LATENT HEAT E = m x lf OR lf = E / m Joules/gram The amount of heat
lf (latent heat of fusion) P . t = m x lf OR P . t = lf required to solid into
lv (latent of m liquid with out
E = m x lV lf = E / m changing the
vaporization)
temperature
Is called latent heat
of fusion
LATENT HEAT E = m x lf OR lf = E / m when power Joules/gram
P . t = m x lf OR P . t = lf of heater and
lf (latent heat of fusion)
m time of j/g The amount of heat
lv (latent of when power of heater and time heating is required to liquid
of heating is given given into Gas with out
vaporization)
E = m x lV OR lf = E / m changing the
when power temperature
when power of heater and time is of heater and Is called latent heat
given time is given of Vaporization
SPEED OF V = Distance/time (without echo) m/s
Sound is a form of
SOUND V= d/t energy which
S=2xdistance/time (with echo) m/s produce by any
vibrating object
V = 2d/t
Frequency Frequency= 1/time Hz Number of waves
Cycle/sec passing through any
close surface in one
f=1/T second
Time Time = 1 / frequency sec
The time of one
T = 1/ f complete cycle
When speed
R.F = speed of light in air(vacuum) is given in m/s
Speed of light in medium
light move The ratio of the
from less speed of light
dense to No unit in air or vacuum to
Refractive index = sin i/ sin r that in
Refractive index dense
medium another medium.
Refractive index= sin r/sin i
light move
For critical angle
from dense
Refractive index= 1/sinC
to less dense
medium
Speed of wave Speed = frequency (Hz) x m/s Air =330-340m/s
wavelength(m) Water =1500m/s
Concrete=5000m/s
v= f.λ Steel = 5000-
7000m/s
Electric charge Electric charge = current x time Coulomb
Q=I.t C
Electric Current Electric current = Electric charge Ampere Rate of flow of
time electric charge in a
I = Q/t A conductor is called
current
Ohms law VOLTAGE= CURRENT X RESISTANCE When current Volt voltage across a resistor
V = I .R and is directly proportional to
or its current V ἀ I provided
resistance is Ohms if the physical condition
R = V/I given remain same
Or
ampere
I =v/R
Power Power= voltage x current When current Watt
P= V . I and voltage is The rate of doing
Or given work is called power
V = P/I Volt
I = P/v ampere
Power Power = current2 x resistance When
P = I2 . R resistance Watt The rate of doing
and current is work is called power
Or given
R = P/ I2 Ohms
Ω
Power Power= Voltage2/Resistance When
P = V2/R resistance Watt The rate of doing
and voltage is work is called power
Or given
R = V2 /P (For power
dissipation Ω
Or loss)
Energy Energy= voltage x current x time When voltage Joules
E=V.I. t , current and The ability to do
time is given work is called energy
E=P. t
When Power
and time is
given
Resistance in R = R 1 + R2 + R3 Current Ohms
series for voltage in series combination remain same
V = V1 + V2 + V3 in series
For potential Divider circuit volts
Vout = Vin R2
R1 + R2
-1
Resistance in 1 = 1 + 1 +1 Voltage Ohms -1
= 1 + 1 +1
parallel R R1 R2 R3 remain same R1 R 2 R 3
for two resistor in parallel in parallel
1 = R 1 x R2 circuit
R R1 + R2
for Current in parallel combination
I = I1 + I2 + I3 ampere
Transformer NS = VS WHEN
NP VP number of No unit A device used to
OR turn and transfer electric
NP = VP voltage is energy from one
NS VS given circuit to another
by
magnetic coupling
Power of V S X IS = V P X IP When current
transformer OR and voltage is No unit
IP = VS given
IS VP
Atomic mass A = atomic The mass of an
Or A
X
z mass atom, usually
Atomic number Z= atomic no expressed in
Z+N = A atomic mass units
Nucleon No Atomic mass = Proton no +
Neutron no
A A–4 4
Alpha decay zX z - 2 X + 2α
A A
Beta decay X
z X + 0-1β
z +1
A A
X*
z zX + 00ϓ
Gama decay