JavaScript HTML DOM
With the HTML DOM, JavaScript can access and change all
the elements of an HTML document.
The HTML DOM (Document Object
Model)
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates
a Document Object Model of the page.
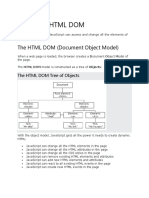
The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects:
The HTML DOM Tree of Objects
With the object model, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic
HTML:
JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
JavaScript can remove existing HTML elements and attributes
JavaScript can add new HTML elements and attributes
JavaScript can react to all existing HTML events in the page
JavaScript can create new HTML events in the page
What is the DOM?
The DOM is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard.
The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents:
"The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral
interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the
content, structure, and style of a document."
The W3C DOM standard is separated into 3 different parts:
Core DOM - standard model for all document types
XML DOM - standard model for XML documents
HTML DOM - standard model for HTML documents
What is the HTML DOM?
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for
HTML.
It defines:
The HTML elements as objects
The properties of all HTML elements
The methods to access all HTML elements
The events for all HTML elements
In other words:- The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add,
or delete HTML elements.
JavaScript - HTML DOM
Methods
HTML DOM methods are actions you can perform (on HTML
Elements).
HTML DOM properties are values (of HTML Elements) that you can
set or change.
The DOM Programming Interface
The HTML DOM can be accessed with JavaScript (and with other
programming languages).
In the DOM, all HTML elements are defined as objects.
The programming interface is the properties and methods of each object.
A property is a value that you can get or set (like changing the content of an
HTML element).
A method is an action you can do (like add or deleting an HTML element).
Example
The following example changes the content (the innerHTML) of
the <p> element with id="demo":
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>My First Page</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
[Link]("demo").innerHTML = "Hello World!";
</script>
</body>
</html>
In the example above, getElementById is a method, while innerHTML is
a property.
The getElementById Method
The most common way to access an HTML element is to use the id of the
element.
In the example above the getElementById method used id="demo" to find the
element.
The innerHTML Property
The easiest way to get the content of an element is by using
the innerHTML property.
The innerHTML property is useful for getting or replacing the content of HTML
elements.
The innerHTML property can be used to get or change any HTML element,
including <html> and <body>.
JavaScript HTML DOM
Document
The HTML DOM document object is the owner of all other objects in
your web page.
The HTML DOM Document Object
The document object represents your web page.
If you want to access any element in an HTML page, you always start with
accessing the document object.
Below are some examples of how you can use the document object to access
and manipulate HTML.
Finding HTML Elements
Method Description
[Link](id) Find an element by element
id
[Link](name) Find elements by tag name
[Link](name) Find elements by class name
Changing HTML Elements
Property Description
[Link] = new html Change the inner HTML of an
content element
[Link] = new value Change the attribute value of
an HTML element
[Link] = new style Change the style of an HTML
element
Method Description
[Link](attribute, value) Change the attribute value of
an HTML element
Adding and Deleting Elements
Method Description
[Link](element) Create an HTML element
[Link](element) Remove an HTML element
[Link](element) Add an HTML element
[Link](new, old) Replace an HTML element
[Link](text) Write into the HTML output stream
Adding Events Handlers
Method Description
[Link](id).onclick = function(){code} Adding event
handler code to an
onclick event
Finding HTML Objects
The first HTML DOM Level 1 (1998), defined 11 HTML objects, object
collections, and properties. These are still valid in HTML5.
Later, in HTML DOM Level 3, more objects, collections, and properties were
added.
Property Description DOM
[Link] Returns all <a> elements that have a name 1
attribute
[Link] Deprecated 1
[Link] Returns the absolute base URI of the 3
document
[Link] Returns the <body> element 1
[Link] Returns the document's cookie 1
[Link] Returns the document's doctype 3
[Link] Returns the <html> element 3
[Link] Returns the mode used by the browser 3
[Link] Returns the URI of the document 3
[Link] Returns the domain name of the document 1
server
[Link] Obsolete. 3
[Link] Returns all <embed> elements 3
[Link] Returns all <form> elements 1
[Link] Returns the <head> element 3
[Link] Returns all <img> elements 1
[Link] Returns the DOM implementation 3
[Link] Returns the document's encoding 3
(character set)
[Link] Returns the date and time the document 3
was updated
[Link] Returns all <area> and <a> elements that 1
have a href attribute
[Link] Returns the (loading) status of the 3
document
[Link] Returns the URI of the referrer (the 1
linking document)
[Link] Returns all <script> elements 3
[Link] Returns if error checking is enforced 3
g
[Link] Returns the <title> element 1
[Link] Returns the complete URL of the 1
document
JavaScript HTML DOM
Elements
This is teaching you how to find and access HTML elements in an
HTML page.
Finding HTML Elements
Often, with JavaScript, you want to manipulate HTML elements.
To do so, you have to find the elements first. There are several ways to do this:
Finding HTML elements by id
Finding HTML elements by tag name
Finding HTML elements by class name
Finding HTML elements by CSS selectors
Finding HTML elements by HTML object collections
Finding HTML Element by Id
The easiest way to find an HTML element in the DOM is by using the element
id.
This example finds the element with id="intro":
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<p id="intro">Finding HTML Elements by Id</p>
<p>This example demonstrates the <b>getElementsById</b> method.</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const element = [Link]("intro");
[Link]("demo").innerHTML =
"The text from the intro paragraph is: " + [Link];
</script>
</body>
</html>
If the element is found, the method will return the element as an object (in
element).
If the element is not found, element will contain null.
Finding HTML Elements by Tag Name
This example finds all <p> elements:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<p>Finding HTML Elements by Tag Name.</p>
<p>This example demonstrates the <b>getElementsByTagName</b>
method.</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const element = [Link]("p");
[Link]("demo").innerHTML = 'The text in first
paragraph (index 0) is: ' + element[0].innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
This example finds the element with id="main", and then finds all <p> elements
inside "main":
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<div id="main">
<p>Finding HTML Elements by Tag Name</p>
<p>This example demonstrates the
<b>getElementsByTagName</b> method.</p>
</div>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const x = [Link]("main");
const y = [Link]("p");
[Link]("demo").innerHTML =
'The first paragraph (index 0) inside "main" is: ' +
y[0].innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Finding HTML Elements by Class
Name
If you want to find all HTML elements with the same class name,
use getElementsByClassName().
This example returns a list of all elements with class="intro".
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<p>Finding HTML Elements by Class Name.</p>
<p class="intro">Hello World!</p>
<p class="intro">This example demonstrates the
<b>getElementsByClassName</b> method.</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const x = [Link]("intro");
[Link]("demo").innerHTML =
'The first paragraph (index 0) with class="intro" is: ' +
x[0].innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Finding HTML Elements by CSS
Selectors
If you want to find all HTML elements that match a specified CSS selector (id,
class names, types, attributes, values of attributes, etc), use
the querySelectorAll() method.
This example returns a list of all <p> elements with class="intro".
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<p>Finding HTML Elements by Query Selector</p>
<p class="intro">Hello World!.</p>
<p class="intro">This example demonstrates the
<b>querySelectorAll</b> method.</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const x = [Link]("[Link]");
[Link]("demo").innerHTML =
'The first paragraph (index 0) with class="intro" is: ' +
x[0].innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Finding HTML Elements by HTML
Object Collections
This example finds the form element with id="frm1", in the forms collection, and
displays all element values:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTML DOM</h2>
<p>Finding HTML Elements Using <b>[Link]</b>.</p>
<form id="frm1" action="/action_page.php">
First name: <input type="text" name="fname" value="Donald"><br>
Last name: <input type="text" name="lname" value="Duck"><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<p>These are the values of each element in the form:</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const x = [Link]["frm1"];
let text = "";
for (let i = 0; i < [Link] ;i++) {
text += [Link][i].value + "<br>";
}
[Link]("demo").innerHTML = text;
</script>
</body>
</html>