Elements of Mechanical Engineering
Dr. Ranjeet Kumar Sahu
Assistant Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
National Institute of Technology Karnataka
Surathkal, Mangaluru, India
1
Heat engines
• Heat engine device which converts chemical energy of fuel into
heat energy & heat energy converted into mechanical work
• Heat engines are mainly classified into two types:
Internal combustion (EC) engines
External combustion (IC) engines
Contd….
IC engines
• Combustion of fuel takes place inside the cylinder
Examples Applications
Petrol engine Road vehicles
Diesel engine Locomotives
Gas turbine (Open) Aircraft
Rocket engine Space
Wankel engine Pump sets
Contd….
EC engines
• Combustion of fuel takes place outside the cylinder
Examples Applications
Steam engine Locomotives; Ships
Steam turbine Electric power generation
Hot air engine Submarines
Gas turbine (Closed) Aircraft
Contd….
Comparison of IC and EC engines
IC engines EC engines
Fuel combustion occurs inside cylinder Fuel combustion occurs outside cylinder
Compact in size and more efficient Larger in size and less efficient
Low initial cost More initial cost
Working fluid is mixture of air and fuel Working fluid is steam/gas
Less time required for starting More time required for starting
Costly fuels are required Cheaper fuels may be used
Contd….
Classification of heat engines
Contd….
Classification of IC engines
• Type of fuel used Petrol; diesel; gasoline
• Type of ignition SI and CI
• Cycle of operation 2-stroke engine; 4-stroke engine
• Nature of thermodynamic cycle Otto cycle engine; Diesel
cycle engine; Dual cycle engine
• Speed of engine Low speed; medium speed; high speed
Contd….
• Method of cooling Air cooled; water cooled;
• Number of cylinders Single cylinder; multi-cylinder
• Cylinder arrangement In-line or straight engine
V-type engine
In-line or straight engine V-type engine
Components of IC engine
Cylinder head Piston pin Crankshaft Valves
Cylinder Connecting rod Crankcase Valve mechanisms
Piston Crank pin Main bearing Governor
Piston rings Crank Flywheel Fuel pump
Engine nomenclature
• Bore inside diameter of cylinder
• TDC top most position of piston
in cylinder away from crank
• BDC Lowest position of piston near
to crank
• Stroke Distance travelled by piston
from TDC to BDC or vice-versa
• Clearance volume Space between cylinder head and TDC of
piston
Contd….
• Swept volume/displacement volume volume displaced by piston
in moving between TDC and BDC
• Compression ratio (r) ratio of total cylinder volume to clearance
volume
• Piston speed average speed of the piston
• MEP MEP = Wnet / (V – Vc)
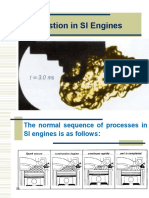
Engine operation
• 4-stroke cycle engine and 2-stroke cycle engine?
• SI engine and CI engine?
4-stroke cycle
SI engine
OR
4-stroke cycle
Petrol engine
Actual P-V diagram
Ideal P-V diagram
Ideal Valve Time Diagram Actual Valve Time Diagram
Contd….
4-stroke cycle
CI engine
OR
4-stroke cycle
Diesel engine
I.V. Inlet valve E.C. Engine cylinder
E.V. Exhaust valve C.R. Connecting rod
F.I. Fuel injector C Crank
Invented by Rudolf Diesel
(1892)
Higher compression ratio
Charge is air alone, no
carburetor.
No spark plug
Fuel is injected using fuel
pump and injector
Contd….
2-stroke cycle petrol engine 2-stroke cycle diesel engine
Contd….
Comparison of 4-stroke and 2-stroke engines
4-stroke engine 2-stroke engine
Cyclic operation is completed in four Cyclic operation is completed in two
strokes of the piston strokes of the piston
Power produced is less for same size Power produced is more for same size
Thermal efficiency is high Thermal efficiency is low
Valves used Ports used
Cooling and lubrication are less required Cooling and lubrication are more required
Costly for same power output Cheaper for same power output
Volumetric efficiency is more Volumetric efficiency is less
Contd….
Comparison of SI and CI engines
SI engine CI engine
Ignition system with spark plug is Ignition system with spark plug is not
required required
Petrol is used Diesel is used
Works on Otto cycle Works on Diesel cycle
Air fuel ratio – 10:1 to 20:1 Air fuel ratio – 18:1 to 100:1
Fuel supplied by carburetor Fuel supplied by fuel injection system
Compression ratio – 6 to 10 Compression ratio – 12 to 24
Thermal efficiency is low (order 25%) Thermal efficiency is low (order 40%)
Light in weight Heavy in weight
Contd….
Engine capacity
• Engine capacity swept volume or displacement volume
• Measured in cc or litres
• For multi-cylinder engines Engine capacity = Vs × no. of
cylinders
• More engine capacity More power and torque can be produced
at lower rpm consume more fuel
Firing order
Firing order refers to the sequence in which the charge in the various
cylinders of a multi cylinder engine is ignited and burnt.
Cylinders are ignited at the alternative ends of the crankshaft. This
enables the crankshaft to be stressed more or less uniformly along its
length.
When designing an engine, choosing an appropriate firing order is
critical
to minimizing vibration,
to improve engine balance and
achieving smooth running,
for long engine fatigue life and user comfort,
heavily influences crankshaft design.
Contd….
Fuel supply system in SI engine
• Fuel supply tank
• Fuel pump
• Fuel pipe lines
• Fuel filter
• Air filter
• Carburettor
Note: Carburetion
25
Contd….
Fuel supply system in CI engine
• Fuel supply tank
• Fuel feed pump
• Fuel filters
• FIP
• Fuel pipe lines
• Fuel Injector
• Air filter
26
Contd….
Functions of a fuel injection system
• Filter the fuel
• Measure the correct quantity of fuel to be injected
• Time the fuel injection
• Control the rate of fuel injection
• Atomise the fuel to fine particles
• Properly distribute the fuel into combustion chamber
27
Contd….
Lubrication system
• Crankshaft bearings
• Big end bearings
• Small end bearings
• Piston rings and cylinder walls
• Camshaft and camshaft bearings
28
Contd….
Cooling system
• Air cooling
• Water cooling
29