EC3032 POWER ELECTRONICS
LESSON 4: UNCONTROLLED THREE PHASE RECTIFIERS
DR RUWAN CHANDRASENA
SLIDES CREDIT TO DR SUJEEWA HETTIWATTA
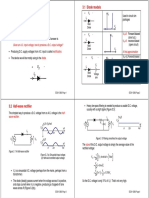
COMPARISON OF AVERAGE (DC) VOLTAGE OUTPUT
FROM SINGLE PHASE RECTIFIERS
SINGLE PHASE – HALF WAVE SINGLE PHASE – FULL WAVE
• Input: 𝑣𝑠 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 • Input: 𝑣𝑠 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡
𝑉𝑚 2𝑉𝑚
• Output (DC): 𝑉𝐴𝑉𝐺 = 𝑉𝐷𝐶 = 𝜋
• Output (DC): 𝑉𝐴𝑉𝐺 = 𝑉𝐷𝐶 = 𝜋
• Output ripple (pp) with filter • Output ripple (pp) with filter capacitor:
𝑉𝑚 𝑉𝑚
capacitor: 𝑉𝑟 𝑝𝑝 = 𝑉𝑟 𝑝𝑝 =
𝑅𝐶𝑓 2𝑅𝐶𝑓
2
REQUIREMENT FOR 3-PHASE RECTIFIERS
• Output power from the single-phase rectifiers are limited (up to about 15 kW)
• Higher power outputs (and less voltage ripple) can be obtained by using 3-
phase rectifiers.
3
m - PHASE HALF WAVE RECTIFIER
• Consider the circuit shown with m-
inputs. The m-inputs can be from m-
phase power supply.
• At any given time, the output will be
equal to the highest voltage from any
input.
• At that time, only the diode in that
phase will conduct; all other diodes
will be reverse biased.
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
m - PHASE • Now consider only four phases, with v1 to v4, having four
HALF WAVE arbitrary waveforms. The output will be as shown in figure.
RECTIFIER …
• As seen, at any given time, the output voltage will be equal to the highest input voltage from any phase.
• We can extend the same concept to 3-phase half wave rectifiers.
5
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
THREE-PHASE VOLTAGES
• Three phase voltages can be expressed as vA, vB and vC
• The three phases can also be colour-coded in Red, Yellow and Blue.
• Let us represent:
• 𝑣𝐴 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡
• 𝑣𝐵 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 120𝑜
• 𝑣𝐶 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 240𝑜 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 120𝑜
• The three voltages (vA, vB and vC) are called phase voltages. 6
THREE-PHASE
VOLTAGES …
• If we plot vA, vB and vC as functions
of time, we get the plot shown.
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THREE PHASE HALF
WAVE RECTIFIER
• The circuit diagram of a three-
phase half wave rectifier is as
shown.
• Compare it with a circuit diagram
for a single-phase HWR.
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THREE PHASE HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER – OUTPUT
WAVEFORM
• The output waveform consists of
three pulses within one complete
power cycle.
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
AVERAGE (DC) OUTPUT VOLTAGE FROM A THREE-
PHASE HALF WAVE RECTIFIER
• The output can be calculated using the output waveform.
10
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE RIPPLE (PP)
FROM A THREE-PHASE HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER WITH FILTER CAPACITOR
• It can be shown that:
𝑉𝑠
• 𝑉𝑟(𝑝𝑝) = 3𝑅𝐶𝑓
• In deriving the above formula it is
𝑇
assumed that 𝑅𝐶 ≫ , where T is
3
the period of one power cycle.
11
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
THREE PHASE HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER WITH HIGHLY
INDUCTIVE LOAD
• With a highly inductive load, the
load current can be assumed
constant in steady state operation.
Therefore, the load can be
represented by a current source.
12
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
WAVEFORMS FROM THREE PHASE HALF WAVE
RECTIFIER WITH HIGHLY INDUCTIVE LOAD
13
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
THREE PHASE FULL WAVE RECTIFIER
14
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
THREE PHASE FULL WAVE RECTIFIER
Average voltage Vo can also be found as
15
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
ANOTHER LOOK AT
THE THREE-PHASE
FULL WAVE RECTIFIER
• Each phase is connected as
shown in figure:
16
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
ANOTHER LOOK AT THE
THREE-PHASE FULL
WAVE RECTIFIER
WAVEFORMS
• The output waveform is made up
of parts from most positive and
most negative of the phase
voltages.
• For example, during 30o 90o
the output waveform is made up
of 𝑣𝐴𝐵 since phase A has the
highest voltage and phase B has
the lowest voltage.
17
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
COULD YOU IDENTIFY WHICH
TWO DIODES CONDUCT
DURING EACH PULSE OUTPUT?
Conduction angle Diodes conducting
30o 90o
90o 150o
150o 210o
210o 270o
270o 330o
330o 390o
18
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
TWO DIODES CONDUCT
DURING EACH PULSE OUTPUT
Conduction angle Diodes conducting
30o 90o D1 and D4
90o 150o D1 and D6
150o 210o D3 and D6
210o 270o D3 and D2
270o 330o D5 and D2
330o 390o D5 and D4
• Note that each diode conducts for 120O or for a time
𝑇
period of
3
19
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE
• As can be seen the output consists of
pulses. There are six pulses within one
period (one power cycle).
• The output consists of line-to-line
voltages:
• 𝑣𝐴𝐵 = 𝑣𝐴 − 𝑣𝐵
• 𝑣𝐵𝐶 = 𝑣𝐵 − 𝑣𝐶
• 𝑣𝐶𝐴 = 𝑣𝐶 − 𝑣𝐴
20
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THE LINE-TO-LINE VOLTAGES
• 𝑣𝐴𝐵 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 120𝑜
• 𝑣𝐴𝐵 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 30𝑜
• 𝑣𝐵𝐶 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 120𝑜 − 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 120𝑜
• 𝑣𝐵𝐶 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 90𝑜
• 𝑣𝐶𝐴 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 120𝑜 − 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡
• 𝑣𝐶𝐴 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 150𝑜
21
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THE LINE-TO-LINE
VOLTAGES IN A
PHASOR DIAGRAM
• 𝑣𝐴𝐵 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 30𝑜
• 𝑣𝐵𝐶 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 − 90𝑜
• 𝑣𝐶𝐴 = 3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 150𝑜
22
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
CALCULATING THE
AVERAGE (DC) OUTPUT
VOLTAGE
1 𝑇
• 𝑉𝑜,𝐴𝑉𝐺 = 𝑇 0 𝑣𝑜 𝑡 𝑑𝑡
• Since 𝑣𝑜 has the same shape repeated
six times during period T,
6 𝑇Τ
• 𝑉𝑜,𝐴𝑉𝐺 = 𝑇 𝑇Τ 4 𝑣𝑜 𝑡 𝑑𝑡
12
𝑇 𝑇
• 𝑣𝑜 𝑡 = 𝑣𝐴𝐵 𝑡 from 𝑡 = 12
to 𝑡 = 4
23
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
CALCULATING THE
AVERAGE (DC) OUTPUT
VOLTAGE …
6 𝑇Τ4
• 𝑉𝑜,𝐴𝑉𝐺 =
𝑇 𝑇Τ12
3𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑡 + 30𝑜 𝑑𝑡
• Integrating and simplifying gives us:
3 3
• 𝑉𝑜,𝐴𝑉𝐺 = 𝜋 𝑚
𝑉
• Which is double the value obtained
under three-phase half wave
rectification.
24
• Image credit: https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/three-phase-rectification.html, last accessed on 27 July 2020
THREE PHASE FULL
WAVE RECTIFIER WITH
HIGHLY INDUCTIVE
LOAD
• With a highly inductive load,
the load current can be
assumed constant in steady
state operation. Therefore, the
load can be represented by a
current source.
25
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
WAVEFORMS FROM THREE
PHASE FULL WAVE
RECTIFIER WITH HIGHLY
INDUCTIVE LOAD
• Note the diode labelling (D1
up to D6) in this circuit,
compared to the circuit with the
colored waveforms.
26
• Image credit: Batarseh, I., Harb, A., “Power Electronics: Circuit Analysis and Design”, 2nd Edition, Springer (2018)
NEXT LESSON
• Thyristors and thyristor-controlled circuits
SNH 12 October 2023 27