0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views1 pageElectromagnetism Formulas Explained
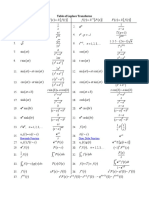
This document contains formulas from electromagnetism, including:
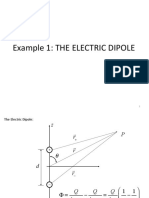
1) The electric potential and electric field from a point charge, and the electric field from a dipole.
2) The magnetic field from a current element and vector potential from a dipole.
3) Relationships between the electric and magnetic fields, electric displacement field, magnetic field strength, electric charge/current density, and magnetic induction.
4) Formulas for the magnetic vector potential, electric dipole moment, magnetic dipole moment, electromagnetic energy density, Poynting vector, and Lorentz transformations.
Uploaded by
Alexander RamirezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
142 views1 pageElectromagnetism Formulas Explained
This document contains formulas from electromagnetism, including:
1) The electric potential and electric field from a point charge, and the electric field from a dipole.
2) The magnetic field from a current element and vector potential from a dipole.
3) Relationships between the electric and magnetic fields, electric displacement field, magnetic field strength, electric charge/current density, and magnetic induction.
4) Formulas for the magnetic vector potential, electric dipole moment, magnetic dipole moment, electromagnetic energy density, Poynting vector, and Lorentz transformations.
Uploaded by
Alexander RamirezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1