www.myengg.
com
Determinants
1
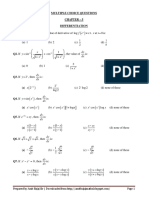
1 a a2 bc 1 b b2 a c = 1 c c2 a b
x +1 3 If 2 x+2 2 3
1.
6.
5 5 x+4
= 0, then x =
(A) 0 (C) 3 abc 2.
(B) a3+ b3 + c3 3 abc (D) (a + b + c)3 7.
(A) 1, 9 (C) - 1, - 9
(B) - 1, 9 (D) 1, - 9
3.
The roots of the equation,
1 4 20 1 2 5 = 0 are : 1 2x 5x2
(A) - 7 (C) 15
g. c
8.
2c
a b c 2a 2b b ca 2c
om
a b a+b
The following system of equations, 3x 2y + z = 0, x 14y + 15z = 0, x + 2y - 3z = 0 has a solution other than, x = y = z = 0 for equal to : (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 5
The value of the determinant,
7 9 79 4 1 41 is : 5 5 55
(B) 0 (D) 27
2a 2b
c a b
(A) - 1, - 2 (C) 1, - 2
0 x+a xa 0
(B) - 1, 2 (D) 1, 2
xb xc 0
.m
4.
If
x+b x+c
= 0, then the
5.
If is the cube root of unity, then
1
2
value of x is : (A) 0 (C) 2
ye ng
9.
(A) (a + b + c)2 (B) (a + b + c)3 (C) (a + b + c) (ab + bc + ca) (D) None of these
a + b a + 2b a + 3b a + 2b a + 3b a + 4 b =
a + 4 b a + 5b a + 6 b
(B) 1 (D) 3
(A) 3 (a + b) (C) 3a + 5b
b+c a b c+a 10. c c
(B) 3 ab (D) 0
= (B) 2 abc (D) 4 abc
1 =
(A) 1 (C)
(B) 0 (D) 2
(A) abc (C) 3 abc
11. One of the roots of the given equation
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
2
x+a b b x+c c a
c a a+b
= 0, is : (B) - (b + c) (D) - (a + b + c)
A1 determinant, A 2 A3
B1 B2 B3
C1 C 2 is : C3
(A) - (a + b) (C) - a
(A) (C) 3
(B) 2 (D) 0
12. If 2x + 3y - 5z = 7, x + y + z = 6, 3x - 4y + 2z = 1, then x =
2 5 7 7 (A) 1 1 6 + 6 3 7 (B) 6 2 3 1 1 3 1 5 1 2 3 1 5 1 2
15. The number of solutions of equations x + y - z = 0, 3x - y - z = 0 and x - 3y + z = 0 is : (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) Infinite 16. The number of solutions of the equations, x + 4y - z = 0, 3x 4y z = 0 and x 3y + z = 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) Infinite
b+c a b a 17. c + a b c b = a+b c a c
1 4
3 4
ye ng
(A) (B) (C) (D)
7 3 5 2 3 5 1 + 1 1 1 (C) 6 1 1 4 2 3 4 2
13. x + ky - z = 0, 3x - ky - z = 0 and x - 3y + z = 0 has non-zero solution for k = (A) - 1 (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 2
.m
a1 14. If = a 2 a3
b1 b2
b3
c1 c2 and A , B , C 1 1 1 c3
denote the co-factors of a 1 , b 1 , c 1 respectively, then the value of the
g. c
x +1
2
5 2 1 + 1
18. If x = cy + bz, y = az + cx, z = bx + ay, where x, y, z are not all zero, then : (A) a2 + b 2 + c 2 - 2 abc = 0 (B) a2 + b 2 + c2 + 2 abc = 0 (C) a2 + b 2 + c2 + 2 abc = 1 (D) a2 + b 2 + c 2 - 2 abc = 1 19. If is a cube root of unity, then a root of the following equation,
x + 2 1 2 1 x+
om
1 4
a3 + b 3 + c3 - 3 abc 3 abc - a3 - b3 - c3 a3 + b 3 + c 3 - a 2 b - b 2 c - c 2 a (a + b + c) (a 2 + b2 + c2 + ab + bc + ca)
= 0, is :
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
3 (A) 1 (C) 2 (B) (D) 0 (A) (B) (C) (D) A O, B = O A = O, B O A = O or B = O None of these
20. In a skew-symmetric matrix, the diagonal elements are all : (A) Different from each other (B) Zero (C) One (D) None of these 21. If A, B, C are three n n martices, then (ABC) = (A) A B C (B) C B A (D) B A C (C) B C A
1 2 22. If M = and M2 M I2 = O, 2 3 then = (A) - 2 (B) 2 (C) - 4 (D) 4
3 2 1 27. Inverse of the matrix 4 1 1 2 0 0
is :
2 3 1 1 3 5 3 (B) 7 4 6 (A) 3 7 2 4 5 4 2 7 1 2 4 2 3 1 2 (D) 8 4 5 (C) 5 7 3 5 2 2 4 5
1 0 0 23. If A = 0 1 0 , then A2 = a b 1
w
n n (B) 0 n
1 1 (D) 0 n
1 1 24. If A = , then A n = 0 1
.m
(A) Unit matrix (B) Null matrix (C) A (D) - A
1 n (A) 0 1
n 1 (C) 0 n
ye ng
g. c
then = (A) - 2 (C) 2
4 6 1 2 4 3 0 2 , B = 0 1 and 28. A = 1 2 5 1 2
3 C = 1 , then the expression which 2
is not defined is : (A) A 2 + 2B 2A (C) B C
om
(B) CC (D) AB
1 1 25. If A = , then A2 = 1 1 (A) A (B) 2 A (C) - A (D) - 2 A
1 3 + 2 8 is singular, 29 . If the matrix 2 4 3 5 10
(B) 4 (D) - 4
26. AB = O, if and only if :
30. Out of the following a skewsymmetric matrix is :
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
4
0 4 5 (A) 4 0 6 5 6 0 1 4 5 (B) 4 1 6 5 6 1
(A) (B) (C) (D)
A A A A
singular matrix non-singular matrix orthogonal matrix diagonal matrix
1 4 5 i + 1 4 5 4 2 6 (D) 4 i 6 (C) 5 6 3 5 6 i
1 34. If A = , then for what value 1 of , A2 = O (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) - 1 (D) 1
.m
33. If A and B are non-singular matrices, then : (A) (AB) -1 = A -1 B -1 (B) AB = BA (C) (AB) = A B (D) (AB) -1 = B -1 A -1
1 2 0 1 0 5 , then : 35. If A = 2 5 0
(A) A = A (C) A = 2 A
(B) A = - A (D) None of these
36. If A, B, C are three square matrices such that AB = AC imples B = C, then the matrix A is always :
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
ye ng
1 0 4 1 32. If A = and I = 0 1 , then 3 2 2 A - 6A = (A) 3 I (B) 5 I (C) - 5 I (D) None of these
g. c
(C) A -1 =
(A) Unitary (C) Nilpotent
39. From the following find the correct relation . (A) AB = A B (B) AB = B A
adj A A -1 (D) (AB) = A -1 B -1
40. If A is a square matrix of order 3, then the true statement is (where I is unit matrix) . (A) det (- A) = - det A (B) det A = 0 (C) det (A + I) = 1 + det A (D) det 2A = 2 det A 41. If k is a scalar and I is a unit matrix of order 3, then adj. (k I) = (A) k3 I (B) k2 I 3 (C) - k I (D) - k2 I
0 5 4 0 42. If A = (1, 2, 3) & B = 2 1 1 3 2
om
31. If AB = C, then matrices A, B, C are (A) A2 3 , B3 2 , C2 3 (B) A3 2 , B 2 3 , C3 2 (C) A3 3 , B 2 3 , C3 3 (D) A 3 2 , B2 3 , C3 3
2 1 / 3 3 6 37. If A = , B = 0 1 0 2 x 3 and AB = I, then x = (A) - 1 (B) 1 (C) 0 (D) 2
1 2 38. The matrix A = 1 2
1 2 is : 1 2
(B) Orthogonal (D) Involutary
www.myengg.com
Determinants
5 then AB =
0 5 4 0 4 2 (A) 3 9 6 3 (B) 1 1
46. Adjoint of the matrix,
4 3 3 0 1 is : N= 1 4 4 3
(C) [ 2 1 4]
0 5 8 0 4 3 (D) 1 6 6
(C)
i 0 0 2 i
i i (D) 2 i 0
ye ng
g. c
(A) 5 A (C) 16 A
1 1 (A) 1 1
0 i (A) 0 i / 2
i 0 (B) 0 2 i
2 0 0 48. If A = 0 2 0 , then A2 = 0 0 2
1 44. If A = 2 , then AA = 3
0 1 49. If A = and AB = O, then B = 0 0 0 1 (B) 1 0
(A) 14
1 (B) 4 3
.m
1 2 3 (C) 2 4 6 3 6 9
0 1 (C) 1 0
(D) None of these
1 0 0 45. If A = 0 1 0 , then A 2 = 0 0 1
50. If A and B are square matrices of order 2, then (A + B)2 = (A) A2 + 2 AB + B2 (B) A 2 + AB + BA + B2 (C) A2 + 2 BA + B2 (D) None of these
a c -1 51. If A = , then A = d b
(A) Null matrix (B) Unit matrix (C) A (D) 2 A
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
om
0 i 43. If A = i= 0 i / 2
1 , then A 1 =
(A) N (B) 2 N (C) - N (D) None of these 47. If A is a symmetric matrix, then matrix M AM is : (A) Symmetric (B) Slew-symmetric (C) Hermitian (D) Skew-Hermitial
(B) 10 A (D) 32 A
1 0 (D) 0 0
www.myengg.com
Determinants
6
b c 1 a b cd d a b c 1 a d b c d a
(A)
1 0 0 56. The inverse of the matrix 0 1 0 is 0 0 1 0 0 1 (A) 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 (C) 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (B) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 (D) 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 0 3 3 0
(B)
d b 1 c a b cd a (D) None of these
(C)
g. c
2 + 3 +1 3
cos t sin t 52. If R (t) = , then sin t cos t R (s) R (t) = (A) R (s) + R (t) (B) R (st) (C) R (s + t) (D) None of these
53. The element of second row and third
1 2 1 column in the inverse of 2 1 0 is 1 0 1
57. If the matrix
om
1 2 +4
is
(A) - 2 (C) 1
(B) - 1 (D) 2
54. The solution of the equation,
.m
1 1 0 1 x 1 1 1 0 y = is (x, y, z) = 0 1 1 z 2
ye ng
singular, then = (A) - 2 (B) - 1 (C) 1 (D) 2
58. If A is a square matrix of order n and A = kB, where k is a scalar, than A= (A) B (B) k B (C) kn B (D) n B
59. If p 4 + q 3 + r 2 + s + t =
+3 4 , the value of 3
(A) (1, 1, 1) (C) (- 1, 2, 2)
(B) (0, - 1, 2) (D) (- 1, 0, 2)
55. If A denotes the value of the determinant of the square martix A of order 3, then 2 A = (A) - 8 A (B) 8 A (C) - 2 A (D) None of these
t is : (A) 16 (C) 17
(B) 18 (D) 19
cos sin 60. If A = and sin cos
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
7
k 0 A adj. A = then k is equal to 0 k (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) sin cos (D) cos 2 1 a 4 61. If A = , then A is equal to : 0 1
(A) A.P. (C) H.P.
(B) G.P. (D) None of these
4 6 1 2 4 3 0 2 , B = 0 1 65. Let A = 1 2 5 1 2
and C = [ 3 1 2] . The expression which is not definedis : (A) B B (B) CAB (C) A + B (D) A2 + A
1 0 0 66. Let A = 5 2 0 , then the adjoint 1 6 1
1 a (A) 0 1
4
4 4 a (B) 0 4 1 4 a (D) 0 1
g. c
of A is : (C)
2 3 62. The inverse of is : 4 2
(C)
1 2 3 8 4 2
(D)
1 3 2 8 2 4
63. The value of the determinant,
cos(nx) cos( n + 1) x cos(n + 2) x
a2 sin (nx)
.m
ye ng
1 2 3 (A) 8 4 2
1 3 2 (B) 8 2 4
2 5 32 (A) 0 1 6 0 0 2
0 1 0 5 2 0 (D) None of these (C) 1 6 1
x b a x
sin (n + 1) x
sin (n + 2) x
is independent of : (A) n (B) a (C) x (D) None of these 64. The determinant,
a b a + b b c b + c = 0, a + b b + c 0
x b b 67. If 1 = a x b a a x
om
4 a 4 (C) 0 4
1 0 0 (B) 5 2 0 1 6 1
and 1 =
are
given determinants, then : (A) 1 = 3 ( 2)2 (B)
d ( ) = 2 (2)2 dx 1
d ( ) = 3 2 dx 1
if a, b, c are in :
(D) 1 = 3 3/ 2 2
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
8
3 2 68. If A = , then A (adj.) A = 1 4 10 0 (A) 0 10 10 1 (C) 1 10 0 10 (B) 10 0
a b c ka kb kc x y z , then k x k y k z 72. If = p q r kp kq kr
is equal to : (A) (C) 3 k
(B) k (D) k3
(D) None of these
69. If a1x + b1y + c1z = 0, a 2x + b2y + c2z = 0,
a1 a3x + b3y + c3z = 0 and a 2 a3 b1 b2 b3 c1 c2 = 0, c3
3 2 73. The inverse of the matrix is 1 4
2 4 14 14 (A) 1 3 14 14
ye ng
then the given system has : (A) One trivial and one non-trivial solution (B) No solution (C) One solution (D) Infinite solution 70. If A = [ a
b] , B = [ b a ] and
g. c
74. The value of
n 2 Un = n n3
4 (C) 14 1 14
om
2 14 3 14
3 (B) 14 1 14
2 14 4 14
3 (D) 14 1 14
Un, if
2 14 3 14
n=1
1 logx y logx z logy x 1 logy z is : log z x log z y 1
71. For positive numbers x, y and z, the numerical value of the determinant,
a C = , then the correct statement a is : (A) A = - B (B) A + B = A - B (C) AC = BC (D) CA = CB
.m
1 5 2 N + 1 2 N + 1 is : 3N2 3N
(A) 0 (C) - 1
(B) 1 (D) None of these
75. Matrix A is such that A 2 = 2A - I, where I is the identity matrix . Then for n 2, A n = (A) nA - (n - 1) I (B) nA - I (C) 2n - 1 A - (n - 1) I (D) 2n - 1 A - I 76. In a third order determinant, each element of the first column consists of sum of two terms, each element of the second column consists of sum of three terms and each element of the third column consists of sum of four
(A) 0 (C) loge xyz
(B) 1 (D) None of these
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
www.myengg.com
Determinants
9 terms . Then it can be decomposed into n determinants, where n has the value : (A) 1 (B) 9 (C) 16 (D) 24 77. If value of a third order determinant is 11, then the value of the square of the determinant formed by the cofactors will be : (A) 11 (B) 121 (C) 1331 (D) 14641 78. If A and B are two matrices and (A + B) (A - B) = A2 - B 2, then : (A) AB = BA (B) A 2 + B 2 = A 2 - B2 (C) A B = AB (D) None of the above
5 3 6 4 79. A = and B = 2 4 3 6 11 7 (A) 5 10 11 7 (C) 5 10
(B) A + B = A - B (C) A - B = B - A (D) AB = BA 82. If A and B are square matrices of the same order, then : (A) (AB) = A B (B) (AB) = B A (C) AB = O ; if A = 0 or B = 0 (D) AB = O ; if A = 1 or B = 1
then B =
g. c
(A) X = (B) X = (C) X = (D) X =
(A) cos2 . A 2
ye ng
(C) cos2 . I 2
1 1 (B) 1 2
2 0 0 80. If A = 0 2 0 and B = 0 0 2
12 7 (D) 5 10
.m
84. If A and B are order 3 such that then 3 AB = (A) - 9 (C) - 27
1 2 3 0 1 3 , 0 0 2
85. If 2X + 2Y = I and 2X - Y = O, where I and O are unit and null matrices of order 3 respectively, then :
then AB is equal to : (A) 4 (B) 8 (C) 16 (D) 32 81. If A and B are square matrices of same order, then : (A) A + B = B + A
86. The equations, x + 2y + 3z = 1 ,
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
om
1 2 ,Y = 7 7
1 83. If A = tan 2
tan 2 and AB = 1, 1
(B) cos2 . A T 2 (D) None of these
square matrices of A = 1, B = 3, (B) - 81 (D) 81
2 1 ,Y = 7 7 1 2 I,Y = I 7 7
1 2 I ,Y = I 7 7
www.myengg.com
Determinants
10 2x + y + 3z = 2 , 5x + 5y + 9z = 4 have : (A) Unique solutions (B) Infinitely many solutions (C) Inconsistent (D) None of these
a h g x 87. The order of [x y z] h b f y g f c z
8 5 (A) 5 3 8 5 (C) 5 3 8 5 (B) 5 3
8 5 (D) 5 3
3 4 92. If X = , then the value of Xn 1 1 is : 3 n 4 n (A) n n 2 + n 5 n (B) n n
ye ng
1 3 89. 3 10
g. c
is : (A) A
88. If A and B are two matrices such that AB = B and BA = A, then A2 + B2 = (A) 2 AB (B) 2 BA (C) A + B (D) AB =
3n (C) n 1
5 2 -1 93. If A = , then A = 3 1 1 2 (A) 3 5 1 2 (B) 3 5
10 3 (A) 3 1
0 1 4 90. If A = , then A = 1 0
1 3 (C) 3 10
1 3 (D) 3 10
.m
10 3 (B) 3 1
1 2 (C) 3 5
0 1 0 94. The inverse of matrix A = 1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 (A) 0 1
0 0 (C) 1 1
1 1 (B) 0 0
0 1 (D) 1 0
1 0 0 (C) 0 1 0 0 0 1
3 1 91. If A = , then A2 = 1 2
0 1 95. If A = , I is the unit matrix of 0 0
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
om
is : (A) 3 1 (C) 1 3
(B) 1 1 (D) 3 3
( 4 ) n (D) None of these ( 1) n
1 2 (D) 3 5
(B) A T
1 0 0 (D) 1 0 0 0 1 0
www.myengg.com
Determinants
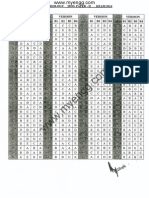
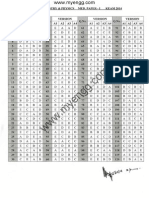
11 order 2 & a, b are arbitrary constants, then (aI + bA)2 is equal to : (A) a 2I + ab A (B) a2I + 2 ab A (C) a 2I + b2A (D) None of these 96. Which of the following is not true ? (A) Every skew-symmetric matrix of odd order is non-singular (B) If determinant of a square matrix is non-zero, then it is non-singular (C) Adjoint of a symmetric matrix is symmetric (D) Adjoint of a diagonal matrix is diagonal 97. Which one of the following statements is true ? (A) Non-singular square matrix does not have a unique inverse (B) Determinant of a non-singular matrix is zero (C) If A = A, then A is a square matrix (D) If A 0, then A . adj A = A(n - 1) where A = [aij]n n ANSWERS 1. A 7. B 13. C 19. D 25. B 31. D 37. B 43. B 49. D 55. A 61. D 67. B 2. D 8. B 14. B 20. B 26. D 32. C 38. C 44. C 50. B 56. B 62. A 68. A 3. B 9. D 15. D 21. B 27. C 33. D 39. B 45. B 51. A 57. D 63. A 69. D 73. 79. 85. 91. 97. A B C D C 74. 80. 86. 92. A C A D 75. 81. 87. 93. A A B B 76. 82. 88. 94. D B C A 77. 83. 89. 95. D B B B 78.A 84.B 90.A 96.A
w
4. A 10. D 16. B 22. D 28. A 34. B 40. A 46. A 52. C 58. C 64. B 70. C
Entrance Exams ,Engineering colleges in india, Placement details of IITs and NITs
QUEST TUTORIALS Head Office : E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439
.m
5. B 11. D 17. B 23. A 29. B 35. B 41. B 47. A 53. B 59. B 65. C 71. A
ye ng
6. D 12.C 18.C 24.A 30.A 36.B 42.C 48.C 54.D 60.B 66.D 72.D
g. c
om