0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views2 pagesOverheating Protection in Transformers
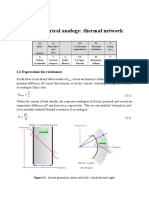
Transformers can overheat from overloads and short circuits, damaging insulation. Temperature sensors measure oil or winding temperature, typically using top-oil or hot-spot measurements, to detect overheating and activate alarms or protective trips. Fiber optic cables now directly measure winding temperature for more accurate overheating protection.
Uploaded by
Izzat HaziqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views2 pagesOverheating Protection in Transformers
Transformers can overheat from overloads and short circuits, damaging insulation. Temperature sensors measure oil or winding temperature, typically using top-oil or hot-spot measurements, to detect overheating and activate alarms or protective trips. Fiber optic cables now directly measure winding temperature for more accurate overheating protection.
Uploaded by
Izzat HaziqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2