Test on variable speed petrol engine
AIM:
To conduct variable speed performance test on a four stroke, three cylinder petrol engine and
plot graphs of Brake power, Brake specific fuel consumption, Brake thermal efficiency, Torque
and Volumetric efficiency Vs speed.
DESCRIPTION OF EXPERIMENTAL SET UP:
The setup consists of three cylinder, four stroke, Petrol (MPFI) engine connected to eddy current
type dynamometer for loading. It is provided with necessary instruments for combustion pressure
and crank-angle measurements. These signals are interfaced to computer through engine
indicator for Pθ-PV diagrams. Provision is also made for interfacing airflow, fuel flow,
temperatures and load measurement. The set up has stand-alone panel box consisting of air box,
fuel tank, manometer, fuel measuring unit, transmitters for air and fuel flow measurements,
process indicator, load indicator and engine indicator. Rotameters are provided for cooling water
and calorimeter water flow measurement. The setup enables study of engine performance for
brake power, indicated power, frictional power, BMEP, IMEP, brake thermal efficiency,
indicated thermal efficiency, Mechanical efficiency, volumetric efficiency, specific fuel
consumption, A/F ratio and heat balance.
SPECIFICATIONS:
Engine power : 27.6 Kw
Engine max speed : 5000 RPM
Cylinder bore : 66.5mm
Stroke length : 72.0mm
Connecting rod length : 114 mm
Compression ratio : 9.2:1
Compression type : FCR
Stoke type : Four
No. of cylinders : Three
Speed type : Variable
Cooling type : Water
Dynamometer type : Eddy current
Data acquisition device : USB-6210
Calorimeter used : Pipe in pipe
Fuel density : 740 kg/m^3
Calorific value : 44000 kJ/kg
Orifice coefficient of discharge : 0.60
Sp heat of exhaust gas : 1.00 kJ/kg-K
THEORY:
Spark ignition engines are often used for automotive applications. It is important to understand
brake thermal efficiency, brake mean effective pressure, torque, volumetric efficiency over the
working speed range .For this purpose variable speed test at full load and part load is conducted
.To test the engine at full load throttle valve is kept wide open and brake load is adjusted to
obtain lowest desired speed. The ignition timing may be set at maximum torque for this speed.
The rate of air consumption, fuel consumption & load are recorded at various speeds.
PROCEDURE:
1. Ensure cooling water circulation for eddy current dynamometer, piezo sensor, engine
cooling and calorimeter.
2. Start the set up and run the engine at no load for 4-5 minutes.
3. Gradually increase throttle to full open condition and load the engine simultaneously
maintaining engine speed at @ 5000 RPM.
4. Wait for steady state (for @ 3 minutes) and collect the reading as per Observations
Table
5. Gradually increase the load to decrease the speed in steps of @500 RPM up to @ 2000
RPM and repeat the observations.
6. Estimate Brake power, Brake mean effective pressure, Air/Fuel ratio, Brake thermal
efficiency, Volumetric efficiency, Brake specific fuel consumption at various speeds and
plot graphs
OBSERVATION TABLE:
Engine make Maruti
Orifice diameter 0.035 Cylinder diameter (m),D 0.0685
(m)
Dynamo. arm length (m) 0.21 Stroke(m),L 0.0725
Coeff.of discharge for orifice,Cd 0.6 No of cylinders 3
Ambient temperatue (Deg C) 30 No.of 2
rev./cycle
Fuel density(kg/m^3) 740
Fuel Calorific value (KJ/kg) 44000
Engine Load Mano.defle.(m Fuel Engine Calo. T1 T2 T3 T4 T5
Speed (Kg) m) flow cooling water
(Rpm) (Secs water (Lph)
/ (Lph)
100m
l.)
2539
3000
3500
4000
4450
T1= Engine water inlet temperature (Deg C)
T2= Engine water outlet temperature (Deg C)
T3= Calorimeter water outlet temperature (Deg C)
T4=Exhaust gas inlet to calorimeter ((Deg C)
T5=Exhaust gas outlet to calorimeter ((Deg C)
CALCULATIONS:
1) Torque (T) = Weight (Kg) ×g(9.81 m/s2) ×arm length(m)
× . × ×
2) Brake Power (BP) = (kW)
×
3) Brake mean effective pressure (bar) =
× × × !"# $×
BP'kW*×3600
4) Brake specific fuel consumption(Bsfc) =
Fuel 2low rate 'Kg/hr*
= <='>?*
5) Brake thermal efficiency IJ
@ABC 2CDE FGHB ×NOPQRS@SN TOPUV Q@ @UVP
KLM
[# "
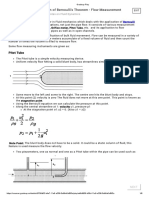
6) Mass flow rate of air (ma) = Cd × (pi/4) ×d2 × W2Yℎ' * ×Aden (Kg/sec)
\# "
Cd=Coefficient of discharge of orifice plate=0.6
d=Diameter of orifice plate=0.035 m
Wden=Density of water =1000 Kg/m3
Aden=Density of air= Kg/m3
7) Mass flow rate of fuel(mf) = (100 ml×10-6 × ρfuel) /t (Kg/sec)
ρfuel = Density of fuel=740 Kg/m3
t = Time required for consumption of 100 ml (sec)
]
8) Air Fuel ratio =
^_`` abcd e_fg ca _he'i_*
9) Volumetric efficiency (%) = jh 2 n
4
×l ×m× 2 ×noipgeca qrbhstge`×'utgs/60*
10) Heat Balance Sheet-
a) Heat supplied by the fuel =mf × Cv (kW) (100 %)
Cv= Calorific value of fuel = 44000(KJ/Kg)
mf=Mass flow rate of fuel(Kg/sec)
b) Heat utilized for useful work =BP (kW) ( BP/(mf*Cv) %)
c) Heat carried away by cooling water = MFW × Cpw × 'v2 − v1* (kW)
(% Contribution)
MFW=Mass flow rate of cooling water in jacket= (Kg/sec)
Cpw=Specific heat of water
T1= Engine water inlet temperature (Deg C)
T2= Engine water outlet temperature (Deg C)
d) Heat carried away by exhaust gases =mg ×Cpg × (T5-Tatm) (kW)
(% Contribution)
mg×Cpg is estimated from energy balance across the calorimeter
mg×Cpg ×(T5-T6) = Mw × Cpw ×(T4-T3)
mg= Mass flow rate of exhaust gas
Cpg=Specific heat of exhaust gas
MW=Mass flow rate of cooling water to engine jacket
Cpw=Specific heat of cooling water
e) Unaccounted losses due to radiation =Heat supplied – Heat utilized
= (a-(b + c +d)) kW
(% Contribution)
RESULT TABLE
N BP BMEP Brake Torque Volumetric Air/ Heat Heat Heat Heat loss
(rpm) (kW) (bar) Thermal N-m Efficiency Fuel To carried carried unaccounted
Efficiency (%) ratio useful away away (%)
(%) work by by
(%) cooling exhaust
water gases
(%) (%)
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
GRAPHS
Plot graphs of 1) Speed Vs BP
2) Speed Vs BMEP
3) Speed Vs Brake Thermal Efficiency
4) Speed Vs Brake Specific fuel consumption
5) Speed Vs Air fuel ratio
6) Speed Vs Volumetric efficiency
7) Speed Vs Heat carried away by cooling water
8) Speed Vs Heat carried away by exhaust gases
9) Speed Vs Unaccounted heat loss
CONCLUSION