0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesBet File - Verification of Superposition Theorem
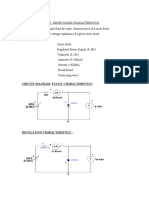
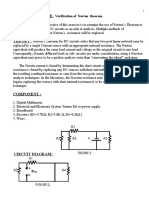
The document describes an experiment to verify the superposition theorem for a circuit with multiple voltage sources. The superposition theorem states that the total current through a branch is equal to the sum of the currents contributed by each independent source. The experiment involves measuring the current through a resistor branch with both sources active, then with one source removed and the other active, and vice versa. The results are compared to verify whether they match the total current predicted by the superposition theorem.
Uploaded by
akashdeep tickooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views6 pagesBet File - Verification of Superposition Theorem
The document describes an experiment to verify the superposition theorem for a circuit with multiple voltage sources. The superposition theorem states that the total current through a branch is equal to the sum of the currents contributed by each independent source. The experiment involves measuring the current through a resistor branch with both sources active, then with one source removed and the other active, and vice versa. The results are compared to verify whether they match the total current predicted by the superposition theorem.
Uploaded by
akashdeep tickooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6