Elasticity and Its Applications: © 2002 by Nelson, A Division of Thomson Canada Limited
Uploaded by
Shahrat Farsim ChowdhuryElasticity and Its Applications: © 2002 by Nelson, A Division of Thomson Canada Limited
Uploaded by
Shahrat Farsim ChowdhuryChapter 5
Elasticity and its
Applications
© 2002 by Nelson, a division of Thomson Canada Limited
In this chapter you will…
•• Learn
Learn the
the meaning
meaning of
of the
the elasticity
elasticity ofof
demand.
demand.
•• Examine
Examine what
what determines
determines thethe elasticity
elasticity of
of
demand.
demand.
•• Learn
Learn the
the meaning
meaning of
of the
the elasticity
elasticity ofof
supply.
supply.
•• Examine
Examine what
what determines
determines thethe elasticity
elasticity of
of
supply.
supply.
•• Apply
Apply the
the concept
concept of
of elasticity
elasticity in
in three
three
different
different markets.
markets.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 2
THE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
•• …
… allows
allows us
us to
to analyze
analyze supply
supply and
and
demand
demand with
with greater
greater precision.
precision.
•• …
… is
is aa measure
measure of
of how
how much
much buyers
buyers and
and
sellers
sellers respond
respond to
to changes
changes in
in market
market
conditions
conditions
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 3
Price Elasticity of Demand
•• Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand isis aa measure
measure of of
how
how much
much the
the quantity
quantity demanded
demanded of of aa
good
good responds
responds to to aa change
change in
in the
the price
price of
of
that
that good.
good.
•• Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand is is the
the
percentage
percentage change
change inin quantity
quantity demanded
demanded
given
given aa percent
percent change
change inin the
the price.
price.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 4
The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its
Determinants
•• Availability
Availability of
of Close
Close Substitutes
Substitutes
•• Necessities
Necessities versus
versus Luxuries
Luxuries
•• Definition
Definition of
of the
the Market
Market
•• Time
Time Horizon
Horizon
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 5
The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its
Determinants
•• Demand
Demand tends tends to to bebe more
more elastic:
elastic:
–– the
the larger
larger the
the number
number of of close
close
substitutes.
substitutes.
–– ifif the
the good
good is is aa luxury.
luxury.
–– the
the more
more narrowly
narrowly defined
defined the
the market.
market.
–– the
the longer
longer the
the time
time period.
period.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 6
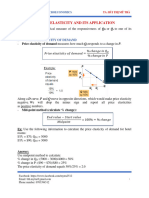
Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
•• The
The price
price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand is is
computed
computed asas the
the percentage
percentage change
change in
in the
the
quantity
quantity demanded
demanded divided
divided byby the
the
percentage
percentage change
change in in price.
price.
Percentage change in quantity demanded
Price elasticity of demand =
Percentage change in price
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 7
The Midpoint Method: A Better Way to
Calculate Percentage Changes and Elasticities
•• The
The midpoint
midpoint formula
formula isis preferable
preferable when
when
calculating
calculating the
the price
price elasticity
elasticity ofof demand
demand
because
because itit gives
gives the
the same
same answer
answer
regardless
regardless of of the
the direction
direction ofof the
the change.
change.
•• point
pointMethod:
Method:AABetter
BetterWay
Wayto
toCalculate
CalculatePercentage
Percentage
Changes and Elasticities
Changes and Elasticities
(Q2 - Q1) / [(Q2 + Q1) / 2]
Price elasticity of demand =
(P2 - P1) / [(P2 + P1) / 2]
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 8
The Midpoint Method: A Better Way to
Calculate Percentage Changes and Elasticities
•• Point
PointA:
A: Price
Price==$4
$4 Quantity
Quantity==120
120
•• Point
PointB:
B: Price
Price==$6
$6 Quantity
Quantity==80
80
•• From
FromPoint
PointAAto
toPoint
PointB:
B:Price
Pricerise
rise==50%
50%and
andQuantity
Quantityfall
fall==33%
33%
•• From
FromPoint
PointBBto
toPoint
PointA:
A:Price
Pricefall
fall==33%
33%and
andQuantity
Quantityrise
rise==50%
50%
(80 - 120) / [(80 + 120)/ 2]
Price elasticity of demand =
(6 - 4) / [(6 + 4)/ 2]
Mid point method
= 1
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 9
A Variety of Demand Curves
•• Inelastic
Inelastic Demand
Demand
–– Quantity
Quantity demanded
demanded does does not
not respond
respond
strongly
strongly to
to price
price changes.
changes.
–– Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand is
is less
less than
than
one.
one.
•• Elastic
Elastic Demand
Demand
–– Quantity
Quantity demanded
demanded responds
responds strongly
strongly
to
to changes
changes in in price.
price.
–– Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand is
is greater
greater
than
than one.
one.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 10
A Variety of Demand Curves
•• Perfectly
Perfectly Inelastic
Inelastic
–– Quantity
Quantity demanded
demanded does
does not
not respond
respond toto
price
price changes.
changes.
•• Perfectly
Perfectly Elastic
Elastic
–– Quantity
Quantity demanded
demanded changes
changes infinitely
infinitely
with
with any
any change
change in
in price.
price.
•• Unit
Unit Elastic
Elastic
–– Quantity
Quantity demanded
demanded changes
changes byby the
the
same
same percentage
percentage as
as the
the price.
price.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 11
A Variety of Demand Curves
•• Because
Because thethe price
price elasticity
elasticity of of demand
demand
measures
measures how how much
much quantity
quantity demanded
demanded
responds
responds to to the
the price,
price, itit is
is closely
closely related
related
to
to the
the slope
slope of
of the
the demand
demand curve. curve.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 12
Figure 5-1 a): Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Price
Demand E=0
$5.00
$4.00
1. An increase
in price…
0 100 Quantity
2. …leaves the quantity demanded unchanged.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 13
Figure 5-1 b): Inelastic Demand
Price
Demand E<1
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 90 100 Quantity
2. … Leads to a 11% decrease in quantity demanded.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 14
Figure 5-1 c): Unit Elastic Demand
Price E=1
Demand
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 80 100 Quantity
2. … Leads to a 22% decrease in quantity demanded.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 15
Figure 5-1 d): Elastic Demand
Price E>1
Demand
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 50 100 Quantity
2. … Leads to a 67% decrease in quantity demanded.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 16
Figure 5-1 e): Perfectly Elastic Demand
Price E=∞
1. At any price above $4, quantity
demanded is zero.
$4.00 Demand
2. At exactly $4, consumers will buy any quantity.
3. At any price below $4, quantity demanded is
infinite.
0
Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 17
Total Revenue and the Price Elasticity of
Demand
•• Total
Total revenue
revenue isis the
the amount
amount paid
paid by
by
buyers
buyers and
and received
received by by sellers
sellers of
of aa good.
good.
•• Computed
Computed as as the
the price
price of
of the
the good
good times
times
the
the quantity
quantity sold.
sold.
TR
TR == PP xx Q
Q
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 18
Figure 5-2: Total Revenue
Price
$4.00
P x Q = $400
(revenue)
Demand
0 100 Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 19
Figure 5-3: How Total Revenue Changes
When Prices Changes: Inelastic Demand
Price
$3.00
P x Q = $400
(revenue)
$1.00
P x Q = $100
(revenue) Demand
0 80 100 Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 20
Figure 5-4: How Total Revenue Changes
When Prices Changes: Elastic Demand
Price
Change in Total Revenue when Price Changes
$5.00
$4.00
Demand
Revenue = $200
Revenue = $100
0 20 50 Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 21
Elasticity and Total Revenue along a Linear
Demand Curve
•• With
With anan elastic
elastic demand
demand curve,
curve, an
an increase
increase
in
in the
the price
price leads
leads to
to aa decrease
decrease in
in quantity
quantity
demanded
demanded that that is
is proportionately
proportionately larger.
larger.
Thus,
Thus, total
total revenue
revenue decreases.
decreases.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 22
Table 5-1. Elasticity and Total Revenue
along a Linear Demand Curve
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 23
Figure 5-5: A Linear Demand Curve
Price
7 Elasticity
is larger
than 1.
6
4
Elasticity
is smaller
3 than 1.
0 4 14 Quantity
2 6 8 10 12
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 24
Other Demand Elasticities
•• Income
Income elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand measures
measures
how
how much much the
the quantity
quantity demanded
demanded ofof aa
good
good responds
responds toto aa change
change inin consumers’
consumers’
income.
income.
•• ItIt is
is computed
computed as as the
the percentage
percentage change
change
in
in thethe quantity
quantity demanded
demanded divided
divided by
by the
the
percentage
percentage change
change in in income.
income.
P e rc e n ta g e c h a n g e
in q u a n tity d e m a n d e d
In c o m e e la s tic ity o f d e m a n d =
P e rc e n ta g e c h a n g e
in in c o m e
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 25
Other Demand Elasticities
•• Types
Types of of Goods
Goods
–– Normal
Normal Goods
Goods
–– Inferior
Inferior Goods
Goods
•• Higher
Higher income
income raises
raises the
the quantity
quantity
demanded
demanded for for normal
normal goods
goods butbut lowers
lowers
the
the quantity
quantity demanded
demanded for for inferior
inferior goods.
goods.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 26
Other Demand Elasticities
•• Goods
Goods consumers
consumers regard
regard asas necessities
necessities
tend
tend toto be
be income
income inelastic
inelastic
–– Examples
Examples include
include food,
food, fuel,
fuel, clothing,
clothing,
utilities,
utilities, and
and medical
medical services.
services.
•• Goods
Goods consumers
consumers regard
regard asas luxuries
luxuries tend
tend
to
to be
be income
income elastic.
elastic.
–– Examples
Examples include
include sports
sports cars,
cars, furs,
furs, and
and
expensive
expensive foods.
foods.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 27
Other Demand Elasticities
•• Cross-Price
Cross-Price elasticity
elasticity of
of demand
demand
measures
measures how how much
much the
the quantity
quantity
demanded
demanded of of aa good
good responds
responds to to aa change
change
in
in thethe price
price of
of another
another good.
good.
•• ItIt is
is computed
computed as as the
the percentage
percentage changechange
in
in thethe quantity
quantity demanded
demanded divided
divided by by the
the
percentage
percentage changechange in in the
the price
price ofof the
the
second
second good.good.
Percentage change
in quantity demanded
Income elasticity of demand =
Percentage change
in the price of
good 2.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 28
PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY
•• Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of supply
supply is is aa measure
measure of of
how
how much
much the
the quantity
quantity supplied
supplied of of aa good
good
responds
responds toto aa change
change inin the
the price
price of
of that
that
good.
good.
•• Price
Price elasticity
elasticity of
of supply
supply is is the
the percentage
percentage
change
change inin quantity
quantity supplied
supplied given
given aa
percent
percent change
change inin the
the price.
price.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 29
The Price Elasticity of Supply and Its
Determinants
•• Ability
Ability of
of sellers
sellers to
to change
change the the amount
amount of of
the
the good
good they
they produce.
produce.
–– Beach-front
Beach-front land
land isis inelastic.
inelastic.
–– Books,
Books, cars,
cars, or
or manufactured
manufactured goods goods are
are
elastic.
elastic.
•• Time
Time period.
period.
–– Supply
Supply is is more
more elastic
elastic inin the
the long
long run.
run.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 30
Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply
•• The
The price
price elasticity
elasticity of
of supply
supply is is computed
computed
as
as the
the percentage
percentage change
change inin the
the quantity
quantity
supplied
supplied divided
divided by
by the
the percentage
percentage
change
change in in price.
price.
P e rc e n ta g e c h a n g e
in q u a n tity s u p p lie d
P ric e e la s tic ity o f s u p p ly =
P e rc e n ta g e c h a n g e in p ric e
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 31
Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply
•• Suppose
Supposean anincrease
increasein
inthe
theprice
priceof
ofmilk
milkfrom
from$1.90
$1.90to
to$2.10
$2.10aalitre
litre
raises
raisesthe
theamount
amountthat
thatdairy
dairyfarmers
farmersproduce
producefrom
from9000
9000toto11
11000
000
LLper month…
per month…
•• ……using
usingthe
themidpoint
midpointmethod,
method,we wecalculate
calculatethe
thepercent
percentchange
changeinin
the price as (2.10 - 1.90) / 2.00 x 100 = 10%
the price as (2.10 - 1.90) / 2.00 x 100 = 10%
•• Similarly,
Similarly,we
wecalculate
calculatethe
thepercent
percentchange
changeininthe
thequantity
quantitysupplied
supplied
as (11 000 - 9000) / 10 000 x 100 = 20%
as (11 000 - 9000) / 10 000 x 100 = 20%
20%
Price elasticity of supply = = 2.0
10%
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 32
Figure 5-6 a): Perfectly Inelastic Supply
Price
Supply E=0
$5.00
$4.00
1. An increase
in price…
0 100 Quantity
2. …leaves the quantity supplied unchanged.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 33
Figure 5-6 b): Inelastic Supply
Price E<0
Supply
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 100 110 Quantity
2. …leads to a 10% increase in quantity
supplied.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 34
Figure 5-6 c): Unit Elastic Supply
Price E=1
Supply
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 100 125 Quantity
2. …leads to a 22% increase in quantity
supplied.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 35
Figure 5-6 d): Elastic Supply
Price E>1
Supply
$5.00
$4.00
1. A 22%
increase in
price…
0 100 200 Quantity
2. …leads to a 67% increase in quantity
supplied.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 36
Figure 5-6 e): Perfectly Elastic Supply
Price E=∞
1. At any price above $4, quantity
supplied is infinite.
$4.00 Supply
2. At exactly $4, producers will supply any quantity.
3. At any price below $4, quantity supplied is zero.
0
Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 37
Figure 5-7: How the price elasticity of supply
can vary
Price
$15
Elasticity is less
than 1
$12
Elasticity is
greater than 1
$4
$3
0 100 200 500
525 Quantity
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 38
THREE APPLICATIONS OF SUPPLY,
DEMAND, AND ELASTICITY
•• Good
Good news
news bad
bad news
news for
for farmers
farmers
•• OPEC
OPEC
•• Drugs
Drugs and
and crime
crime
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 39
Figure 5-8: An Increase in Supply in the
Market for Wheat
Price of
Wheat Increase in Supply
1. When demand is inelastic, an
increase in supply… S1
S2
$3
$2
2. … leads
to a fall in
price…
Demand
100 110 Quantity of Wheat
3. …and a proportionately smaller increase in quantity sold. As a result revenue
falls from $300 to $220.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 40
Figure 5-9: A Reduction in Supply in the
World Market for Oil
(a) Oil Market in the Short Run (b) Oil Market in the Long Run
Price Price
of Oil 1. In the short run, when supply of Oil
and demand are inelastic, a shift
in supply… S2 1. In the long run, when supply
and demand are elastic, a shift in
supply…
S1
S2
S1
P2 P2
P1
P1
2. … leads
Demand
2. … leads to a small
to a large increase in
increase in price…
price…
Demand
Quantity of Oil Quantity of Oil
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 41
Figure 5-10: Policies to Reduce the of Illegal
Drugs (a) Drug Interdiction (b) Drug Education
Price of Price of
Drugs 1. Drug interdiction reduces the
Drugs
supply of drugs… 1. Drug education reduces the
S2 demand for drugs…
S1
Supply
P2
P1
P2
P1
D1
2. … which
2. … which reduces the
raises the price…
price…
D2
Demand
Q2 Q1 Quantity of Drugs Q2 Q1 Quantity of Drugs
3. … and reduces the 3. … and reduces the quantity
quantity sold. sold.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 42
Summary
•• Price
Priceelasticity
elasticityofof demand
demand measures
measureshow how much
much
the
thequantity
quantitydemanded
demandedresponds
respondsto tochanges
changes in in
the
theprice. price.
•• Price
Priceelasticity
elasticityofof demand
demand is iscalculated
calculatedas asthe
the
percentage
percentagechange changein inquantity
quantitydemanded
demandeddivided
divided
by
bythe thepercentage
percentagechange
changein inprice.
price.
•• IfIf aademand
demandcurve
curveis iselastic,
elastic, total
total revenue
revenuefalls
falls
when
whenthe theprice
pricerises.
rises.
•• IfIf itit is
isinelastic,
inelastic, total
total revenue
revenue rises
risesasasthe
theprice
price
rises.
rises.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 43
Summary
•• The
Theincome
incomeelasticity
elasticityof
ofdemand
demandmeasures
measureshowhow
much
much the
thequantity
quantitydemanded
demandedresponds
respondstoto
changes
changesin inconsumers’
consumers’ income.
income.
•• The
Thecross-price
cross-price elasticity
elasticityof
of demand
demandmeasures
measures
how
how much
muchthe
thequantity
quantitydemanded
demandedof of one
onegood
good
responds
respondsto tothe
theprice
priceofof another
anothergood.
good.
•• The
Theprice
priceelasticity
elasticityof
of supply
supplymeasures
measureshow
how
much
much the
thequantity
quantitysupplied
supplied responds
respondstoto changes
changes
in
inthe
theprice.
price.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 44
Summary
•• In
Inmost
mostmarkets,
markets,supply
supplyis ismore
moreelastic
elasticin
inthe
the
long
long run
runthan
thanininthe
the short
short run.
run.
•• The
Theprice
priceelasticity
elasticityof
of supply
supplyis iscalculated
calculated as
asthe
the
percentage
percentagechange
changein inquantity
quantitysupplied
supplieddivided
divided
by
bythe
thepercentage
percentagechange
changein inprice.
price.
•• The
Thetools
toolsof of supply
supplyandanddemand
demand cancan be
beapplied
applied in
in
many
manydifferent
differenttypes
typesof of markets.
markets.
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 45
The End
Mankiw et al. Principles of Microeconomics, 2nd Canadian Edition Chapter 5: Page 46
You might also like
- Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics Chapter 2: Thinking Like An EconomistNo ratings yetChapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics Chapter 2: Thinking Like An Economist3 pages
- Lecture 6: Compensating Wage DifferentialsNo ratings yetLecture 6: Compensating Wage Differentials21 pages
- Elasticity Quiz: Multiple Choice QuestionsNo ratings yetElasticity Quiz: Multiple Choice Questions3 pages
- Elasticity of Demand PPT 100117041420 Phpapp020% (1)Elasticity of Demand PPT 100117041420 Phpapp0236 pages
- Chapter 03 - Interdependence & Gains From TradeNo ratings yetChapter 03 - Interdependence & Gains From Trade18 pages
- The Basic Analysis of Demand and SupplyNo ratings yetThe Basic Analysis of Demand and Supply33 pages
- Understanding Price Elasticity of DemandNo ratings yetUnderstanding Price Elasticity of Demand7 pages
- Demand Elasticity: Imelda B. Cueto Managerial Economics Colegio de San Juan de Letran SbmaNo ratings yetDemand Elasticity: Imelda B. Cueto Managerial Economics Colegio de San Juan de Letran Sbma49 pages
- Section 3b Elasticity of Demand & SupplyNo ratings yetSection 3b Elasticity of Demand & Supply15 pages
- Powerpoint Lectures For Principles of Microeconomics, 9E by Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair & Sharon M. OsterNo ratings yetPowerpoint Lectures For Principles of Microeconomics, 9E by Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair & Sharon M. Oster71 pages
- Ten Principles of Economics: IcroeonomicsNo ratings yetTen Principles of Economics: Icroeonomics22 pages
- Define Economics and Explain Scope of Economics and Different Between Micro and Macro EconomicsNo ratings yetDefine Economics and Explain Scope of Economics and Different Between Micro and Macro Economics7 pages
- Problems Related To Elasticity of Demand and SupplyNo ratings yetProblems Related To Elasticity of Demand and Supply3 pages
- Two Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote CellsNo ratings yetTwo Types of Cells:: Prokaryote Cells and Eukaryote Cells18 pages
- What Is Tissue and What Are The Different Types of Animal Tissue?No ratings yetWhat Is Tissue and What Are The Different Types of Animal Tissue?6 pages
- Intro To Microeconomics, chp1 by N. Gregory MankiwNo ratings yetIntro To Microeconomics, chp1 by N. Gregory Mankiw11 pages
- Plant Cell Culture Protocols 3rd Edition Víctor M. Loyola-Vargas All Chapters Instant Download100% (13)Plant Cell Culture Protocols 3rd Edition Víctor M. Loyola-Vargas All Chapters Instant Download82 pages
- Presentation by Neha Sharma 234-MBA-09 MBA-4th SEMNo ratings yetPresentation by Neha Sharma 234-MBA-09 MBA-4th SEM20 pages
- Statement of Purpose - Uni of BirminghamNo ratings yetStatement of Purpose - Uni of Birmingham3 pages
- Plagiarism Check: Anesthesia Form EvaluationNo ratings yetPlagiarism Check: Anesthesia Form Evaluation56 pages
- Solar System and Atomic Structure OverviewNo ratings yetSolar System and Atomic Structure Overview25 pages
- 4090-9001 Supervised IAM Installation Instructions: Cautions and WarningsNo ratings yet4090-9001 Supervised IAM Installation Instructions: Cautions and Warnings2 pages
- Microwave Signal Attenuation in Harmattan Weather Along Calabar-Akampkpa Line-of-Sight LinkNo ratings yetMicrowave Signal Attenuation in Harmattan Weather Along Calabar-Akampkpa Line-of-Sight Link8 pages
- Heritage Madurai: Luxury Resort in Tamil NaduNo ratings yetHeritage Madurai: Luxury Resort in Tamil Nadu7 pages