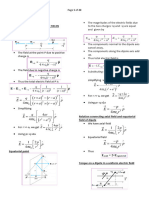
Brinkley: Physics 2426
Formula Sheet
1st 2 pages are EP1(2425) Formulas
Mathematics & Vectors
Motional Definitions
b b 2 4ac (quadratic equation)
x total distance traveled
2a average speed
Where: ax 2 bx c 0 total time
r v
s vav & aav
(Definition of radians) t t
r
A Axi Ay j Az k (Vectors) dx dv d 2 x
v(t ) & a (t ) 2
dt dt dt
r xi yj zk (Position Vector)
A B Ax Bx Ay By Az Bz
Constant linear acceleration
(Scalar or dot product of vectors) (These definitions are applied to each direction independently)
v v0 a t
i j k
r 1
2
v0 v t
1
r v0t at 2
A B det Ax Ay Az
2
2
v v0 2 a r (v is taken as v v )
2 2
Bx B y Bz
(Cross or vector product of vectors)
v AC v AB vBC and v AB vBA
(Relative velocity vectors [notation])
Forces
Work & Potential Energy
F ma
b
Fx max & Fy ma y W a
F dl (work done along path a b)
Fg mg (towards the gravitational body) Wtype Ftype r Ftype r cos
FN N Normal Force (work when force is constant)
(Perpendicular to surface) Wnet K (work energy theorem)
f k k FN (kinetic friction) 1
K mv 2 (Kinetic Energy)
f s s FN (static friction) 2
Fspring kx (Hookes Law) Wc U (For Conservative forces)
Wnc K U (work energy theorem)
F cp macp (in the centripetal direction)
U grav mgy (+y is up; close to surface)
mm
Fg G 1 2 2 (General Force of Gravity) m1m2
r U grav G (Gravitational General)
L r
F A (Youngs) U spring 12 kx 2 (x is stretch/compress dist.)
L0
W
x P F v Fv cos
F S A (Shear) t
L0
V
P B (Bulk)
V0
PHYS 2426 Formulas Page 2
PHYS 2426 Formulas Page 3
Momentum, Impulse & Center of Mass
F
p mv (definition of momentum) I p t (Impulse)
av
dp
F
dt
F
av
p
t
rcm
mi ri r
r dm
(Center of
(Newtons 2nd Law with momentum) M total cm
M
Mass)
Rotational Values
1
Li ne ar Q ua n tit y
x
K rot I 2
v
a
m
2
F
p
1 2 1 1
f ;T ; 2f K total K trans K rot 2
MvPiv I piv 2
T 2 2
vt r r F rF sin
at r I
v2 4 2 L I
acp r 2 r 2 L r p L rmv sin
r T (Point particle)
N
I mi ri r dm
2 2
L
i 1 t
I I com mrcom
2
(Parallel axis Theorem) W
P
t
Harmonics & Oscillations m
T 2
1 2 k
f & 2f & T
T T 2
L
x(t ) A cos(t ) g
Electric Forces &
qenclosed
Fields
dA 0
E
qq qq (Gausss Law)
F k 1 2 2 r k 1 3 2 r
r r E (Surface of
(Coulombs Law) 0
1 a conductor)
k
4 0 E (Line
(Relation between 2 0 r
Coulombs constant & of Charge)
permittivity)
q ne E (Sheet of
2 0
(quantization of Charge)
charge)
F
E &
q0
F qE
q q
E k 2 r k 3 r
r r
(point charge)
p
E k 3 (Electric
z
dipole)
p E (Torque
on a dipole)
U pE
(potential energy of a
dipole)
Charge
;
Volume
Charge
;
Area
Charge
Length
r
E k 2 dq (Con
r
tinuous distribution)
kqz
E
z R2
3
2 2
(ring of charge)
z
E 1
2 0
z R2
2
(Charged disk)
Flux & Gauss
Law
E E dA
(Electric Flux)
Electric Potential # charge carriers 0 ids r Electromagnetic
n dB
U Unit Volume 4r 2 Waves
V i
q v drift & i 1
neA B 0 (long straight c
0 0
f
V E ds 2R
i J ( ne)v drift
wire) c
(Voltage from E-field) V n
i (v is the speed of
kq R (ohms law) B 0 (center of v
V (Point i 4R light in material)
r E 1 1
Charge) & circular arc)
S E B (Pointing
J
L
B ds 0 ienclosed ( 0
pr p cos R & Amperes Law) Vector)
V k 3
4 0 r 2 A E x, t E m sin kx t
nN
r
0 0 (T T0 ) B 0 in &
(Dipole) l B x, t Bm sin kx t
dq V2 (solenoid)
V k P iV i R 1
2
c
r R d B (speed of
induced E ds N 0 0
(Continuous dt
light)
Distribution) Circuits &
V LN ; 2
E rms
Eaverage Kirchhoff i I
s Loop rule, & junction rule di c 0
(electric field from L L
voltage)
Req Ri (series) dt
(where s is U L Lidi 1
2 Li 2 Reflection,
perpendicular to 1 1 Refraction,
t
Ri (parallel)
L
equipotential plane) Req i (t ) 1 e (ch Mirrors &
R Lenses
Capacitance arging)
dq t RC n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 (Sn
C
q i(t ) e t
L (dischargi
V
(Definition
dt R i (t ) i0 e ells Law)
n2
of Capacitance) & ng) sin c (critical
0 A n1
C V (t ) 1 e RC
t
L L (time constant)
d R angle)
(charging) h i
(Parallel Plate m &
capacitor) h p
dq q0 t RC
2 0 L i (t ) e mtot m1 m 2
C dt RC
ln b a Waves
1 1 1
V (t ) V0 e
t
(Cylindrical RC p i f
Capacitor) v f
(discharging) k Quantity If Positive (+
q 2 y x, t A sin kx t p or do (object) Real object
UC 12 CV 2 Magnetism i or di (image) Real image
2C 2
k (Wave number) f (focal) Converging
(Potential Energy) FB q (v B ) &
m (magnification) Upright imag
u E 12 0 E 2 FB i ( L B ) (L is
; y rms
A
(Energy Density of an length of a segment of 2
E-field) wire along the direction of
FT
current flow) v (wave on a string)
v2
Current & FB ma cp q vB m
r m
Resistance ; (linear density)
(circulating in constant l
dq
i & q idt field) P P
dt NiA & I
A 4r 2
J dA
i B (Intensity)
Physical Optics M S 2.00 1030 kg (
(Constructive w/Phase Constants Mass of Sun)
shift) G = 6.67 x 10-11
d sin m (double N.m2/kg2 RME 3.84 108 m (
slits) (Universal Earth-Moon
a sin m (single slit) gravitational distance)
a sin 1.22 (Apert constant)
ure size) RES 1.50 1011 m (
1 0 8.85 1012 C 2 / Nm 2
I I 0 ; I I1 cos2 (Permittivity of free
Earth-Sun distance)
2
(Law of Malus) space)
v uo 1
f Heard f made k
2
8.99 109 N m 2
v u s 4 0 C
(Doppler Shift) (Electrostatic
I Constant)
10dB log
I0
(decibel scale)
e 1.602 10 19 C
0 4 10 7 Tm / A
Conversion (Permeability of free
space)
Factors
1 in = 2.54 cm
1 ft = 0.305 m me 9.11 1031 kg 0.511 MeV
1 mph = 0.447 m/s c2
1 lb = 4.45 Newtons
1 hp = 746 Watts
m p 1.67 1027 kg 938.27 MeV
1 gallon = 3.785 c2
liters
1 m3 = 1000 liters
1 cal = 4.186 J mN 1.0086649u 939.57 MeV
1 Btu = 1055 J c2
mH 1.007825u
u 931.5 MeV
c2
c 2.997 108 m s
Solar System
Data
RE 6.37 106 m
(Radius of Earth)
RM 1.74 106 m
(Radius of Moon)
M E 5.97 10 24 kg (
Mass of Earth)
M M 7.35 10 22 kg (
Mass of Moon)