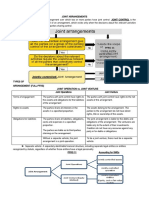
JOINT ARRANGEMENT
• "an arrangement of which two or more parties have joint
control." (PFRS 11.4)
• Essential elements in the definition of joint arrangement:
a. Contractual arrangement
b. Joint control
CONTRACTUAL AGREEMENT
• A contractual agreement for the sharing of joint control over
an investee distinguishes an interest in a joint arrangement
from other types of investments, such as investment in
equity securities measured at fair value (PFRS 9), investment
in associate (PAS 28) and investment in subsidiary (PFRS 3
and PFRS 10).
• PFRS 11 is not applicable without such an agreement.
• The contractual arrangement may be evidenced in various
ways, for example, by a contract, by minutes of discussions
between the parties, or by inclusion in the articles or by-laws.
JOINT CONTROL
• Joint control is "the contractually agreed sharing of control
of an arrangement, which exists only when decisions about
the relevant activities require the unanimous consent of the
parties sharing control." (PFRS 11.7)
• Joint control exists when all the parties sharing joint control
over the arrangement act collectively (together) in
directing the activities that significantly affect the returns
of the arrangement.
TYPES OF JOINT ARRANGEMENT
JOINT OPERATION
• is a joint arrangement whereby the parties that have joint
control of the arrangement have rights to the assets and
obligations for the liabilities of the arrangement.
JOINT VENTURE
• is a joint arrangement whereby the parties that have joint
control of the arrangement have rights to the net assets of
the arrangement.
TYPES OF JOINT ARRANGEMENT
• An entity applies judgment when determining the type of
joint arrangement in which it is involved by:
A. Considering its rights and obligations arising from the
arrangement.
B. Assessing its rights and obligations in relation to the:
• structure and legal form of the arrangement,
• terms of the contractual agreement, and
• other facts and circumstances.
ASSESSMENT OF RIGHTS AND
OBLIGATIONS
Structure and legal form of the arrangement:
• a. A joint arrangement that is not structured through a separate
vehicle is a joint operation.
• b. A joint arrangement in which the assets and liabilities relating
to the arrangement are held in a separate vehicle can be either
a joint venture or a joint operation.
Separate vehicle - "a separately identifiable financial structure,
including separate legal entities or entities recognized by statute,
regardless of whether those entities have a legal personality."
PROBLEM 1
AA, BB and CC sign an agreement to collectively purchase a yacht and to hire
a company to manage and operate the yacht in their behalf. The cost and
revenue earned shall be shared by the three parties based on their ownership
percentage. All major decisions must be agreed by three companies. The cost
of the yacht was 56,000,000 with an estimated life of 20 years. The
management fee in operating the yacht was 11,200,000. Revenue earned
was 18,480,000 on the first year. AA invested 16,800,000 for 30% interest.
1. Compute the share of AA in the revenue of the joint operation for the first
year
2. Compute the share of AA in the expenses of the joint operation for the first
year
3. Compute for the ending capital of AA for the first year
PROBLEM 1
AA, BB and CC sign an agreement to collectively
purchase a yatch and to hire a company to manage
and operate the yatcht in their behalf. The cost and
1. 18,480,000 X 30% =
revenue earned shall be shared by the three parties 5,544,000
based on their ownership percentage. All major
decisions must be agreed by three companies. The 2. 18,480,000 – 11,200,000 –
cost of the yacht was 56,000,000 with an estimated
life of 20 years. The management fee in operating the 2,800,000 X 30% = 1,344,000
yacht was 11,200,000. Revenue earned was
18,480,000 on the first year. AA invested 16,800,000 3. 16,800,000 + 1,344,000 =
for 30% interest.
18,144,000
1. Compute the share of AA in the revenue of the
joint operation for the first year
2. Compute the share of AA in the net income of the
joint operation for the first year
3. Compute for the ending capital of AA for the first
year
PROBLEM 5: PAGE 243
A. JOURNAL ENTRIES
PROBLEM 5: PAGE 243
B. Profit after management fee and bonus
PROBLEM 5: PAGE 243
C. Cash Settlement
CASE # 2
PROBLEM 5: CASE NO. 2 PAGE 243
B. Profit after management fee and bonus
C. Cash Settlement
CASE NO. 3
PROBLEM
• A and B formed a joint operation on January 2024 to operate two
stores to be managed by each joint operator until April 2024. They
agreed to contribute cash for A: 30,000 and B: 20,000.
• P/L are divided in the capital ratio. The following are the relevant
data:
A B
Receipts 78,920 70,695
Disbursement 62,275 65,965
• On April 30, the remaining joint operation non-cash assets in the
hands of the joint operators were sold for 50,000 cash. The joint
operations was terminated and settlement was made between A and
B.
• How was 60,000 was divided between operators?
PROBLEM
A, CAPITAL B, CAPITAL
RECEIPTS 78,920 CONTRIBUTION 30,000 RECEIPTS 70,695 CONTRIBUTION 20,000
DISBURSEMENT 62,275 DISBURSEMENT 65,965
PROFIT 12,825 PROFIT 8,550
78,920 105,100 70,695 94,515
CASH: 26,180 CASH: 23,820
No separate records are maintained
– management account
ACCOUNTING FOR SPECIAL TRANSACTIONS (Advanced Accounting 1) - (by: MILLA
N)
Separate records are maintained
ACCOUNTING FOR SPECIAL TRANSACTIONS (Advanced Accounting 1) - (by: MILLA
N)
JOINT VENTURE
• Equity method is used.
• If JV is SME, choose any of the following
method:
• Equity Method
• FV Method
• Cost Method
IN SUMMARY:
INVESTMENT MODEL
COST MODEL FV MODEL EQUITY MODEL
Investment Cost Investment Investment Investment
Transaction Cost Investment P/L Investment
Dividend Income P/L P/L Investment
Net Income N/A N/A Investment/ P/L
Fair Value N/A Applicable P/L N/A
Impairment Loss Applicable P/L N/A Applicable
JOINT VENTURE FOR SME: PROBLEM
On January 1, 2024, SME J acquired 25% of the equity of L Corporation for
128,000/ SME J shares in the joint control over the relevant activities of the
JV in relation to its operations. Transaction costs of 2% of the purchase
price of the shares were incurred by SME J.
On December 15,2024, L Corporation paid dividend of 18,000 and at year-
end recognized a profit of 60,000
Published price quotations do not exists of L Corp. Using valuation
techniques SME J determined the FV of its investments in L Corp is
140,000. Cost to sell are estimated at 5% of the FV of the investment.
Provide journal entries.
COST MODEL FV MODEL EQUITY
MODEL
Investment Cost Inv in JV 128 Inv in JV 128 Inv in JV 128
Cash 128 Cash 128 Cash 128
Transaction Cost Inv in JV 2.56 P/L 2.56 Inv in JV 2.56
Cash 2.56 Cash 2.56 Cash 2.56
Cash Dividend Dividend Rec 4.5 Dividend Rec 4.5 Dividend Rec 4.5
P/L 4.5 P/L 4.5 Inv. In JV
4.5
Share in Net N/A N/A Inv in JV 15
Profit P/L 15
Fair Value N/A Inv in JV 12 N/A
P/L 12
Impairment Loss N/A N/A P/L 8.060
Inv in JV 8.060