
Read our January issue
This month, a Perspective on data-driven design of synthetic cells, a Comment on bringing biocatalysis to teaching labs, a Thesis on using the term ‘quantum’, and an In Your Element on cyclodextrins.

This month, a Perspective on data-driven design of synthetic cells, a Comment on bringing biocatalysis to teaching labs, a Thesis on using the term ‘quantum’, and an In Your Element on cyclodextrins.

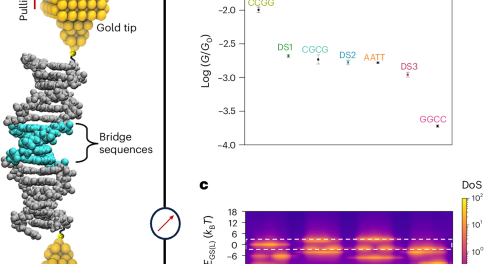
Guidelines for modifying charge transport in DNA are deduced from a series of conductance experiments aimed at exploring the effects of nearest-neighbour base pair interactions on the electronic properties. From these rules, 20-base-pair DNA sequences are designed that maintain high conductance despite their length.