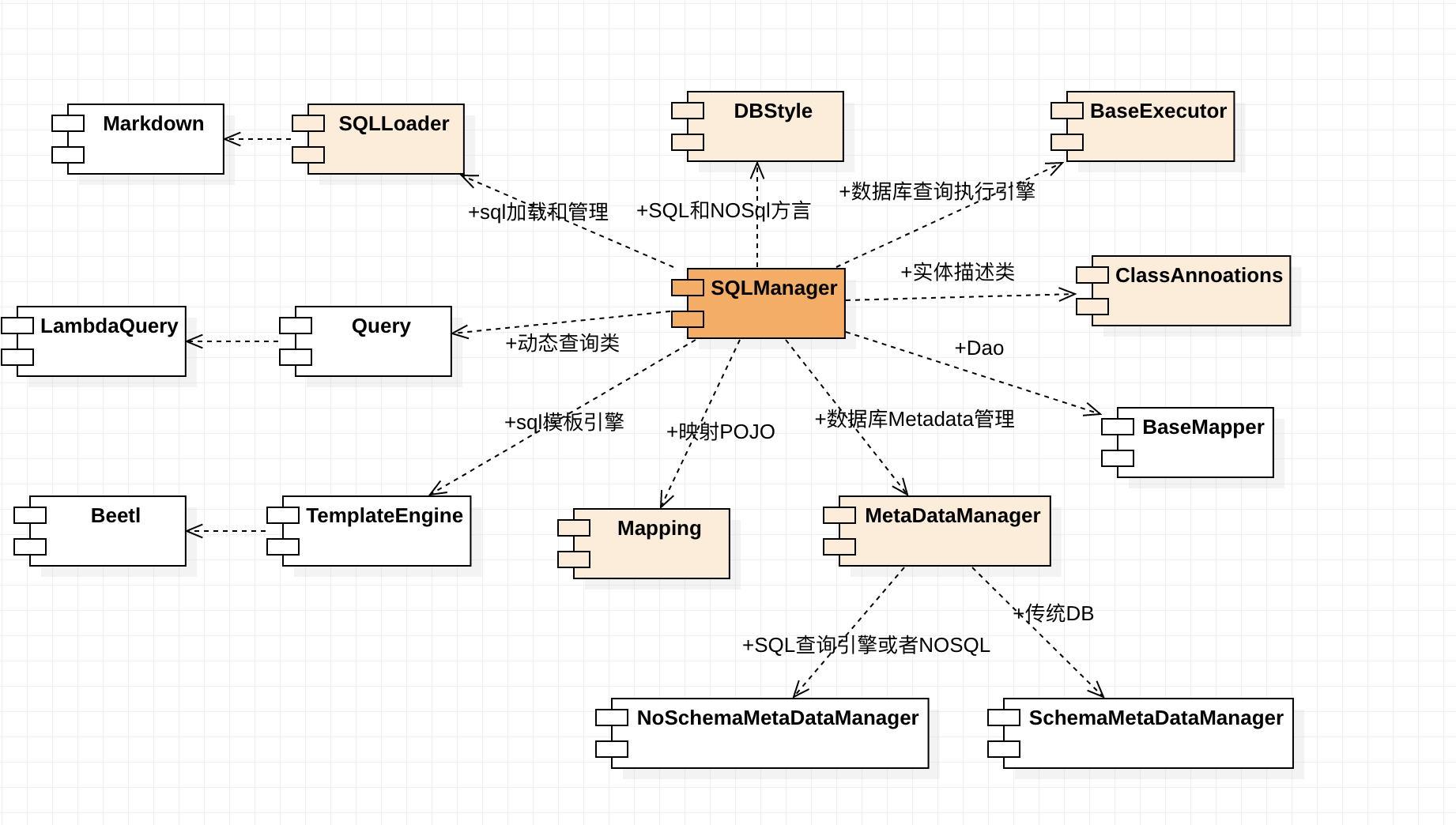
BeetlSQL的目标是提供开发高效,维护高效,运行高效的数据库访问框架,在一个系统多个库的情况下,提供一致的编写代码方式。支持如下数据平台
- 传统数据库:MySQL(国内兼容MySQL协议的各种大数据库),MariaDB,Oracle,Postgres,DB2,SQL Server,H2,SQLite,Derby,神通,达梦,华为高斯,人大金仓,PolarDB等
- 大数据:HBase,ClickHouse,Cassandar,Hive,Doris
- 物联网时序数据库:Machbase,TD-Engine,IotDB
- SQL查询引擎:Drill,Presto,Druid,Trino
- 内存数据库:ignite,CouchBase
BeetlSQL 不仅仅是简单的类似MyBatis或者是Hibernate,或者是二者的综合,BeetlSQL远大理想是对标甚至超越Spring Data,是实现数据访问统一的框架,无论是传统数据库,还是大数据,还是查询引擎或者时序库,内存数据库。
直接在线试用BeetlSQL http://121.42.237.11:8080/beetlsql_online/
- 作者: 闲大赋,Gavin.King,Sue,Zhoupan,woate,darren,蚊子
- 开发时间:2015-07
- 网站 http://ibeetl.com
- qq群 636321946,219324263 252010126
BeetlSQL 核心功能
| BeetlSQL 核心 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| sql-core | 核心包,封装了 JDBC 操作,SQL 文件管理,可扩展注解管理 |
| sql-fetch | 类似 Hibernate 那样提供 @Fetch,@FetchMany 等注解 |
| sql-mapper | mapper 类定义和扩展,用户可以自定义自己的 mapper 和 mapper 的注解 |
| sql-intergration | 整合 Spring,solon,jfinal 等框架,以及例子 |
| sql-query | Query 和 LambdaQuery,用 Java API 构造和使用 SQL |
| sql-mapping | 支持单表,多表与 POJO 的互相映射,支持 json 定义,xml 定义映射方式,或者约定习俗 |
| sql-template | Beetl 模板实现,且支持其他模板语言 |
| sql-gen | 代码生成抽象包,并提供默认实现可以生成 dao,sql 文件,md 文档 |
| sql-db-support | 各种数据库的测试和验证,支持 20+ 数据库。 |
| sql-samples | 包含了上百个使用 beetlsql 的例子 |
| sql-test | 包含了上百个单元测试例子 |
BeetlSQL 最新扩展包
| BeetlSQL 扩展包 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| sql-xml | 高仿 myabtis 的 xml 语法,如果喜欢使用 xml 写 sql 模板的,可以使用此扩展包 |
| sql-accelerator | 性能加速包,通过反射优化,缓存,让 beetlsql 性能提升 50%-200%,接近一半手写 JDBC 的性能 |
| sql-firewall | sql 防火墙,避免不小心写的 sql 破坏数据库 |
| sql-dynamic-table | 支持像访问静态表格那样防火动态表格,简化动态创建表格的业务需求开发 |
| sql-bean-encrypt | 支持 @MD5 ,@AES 等对字段加密解密 |
| sql-rewrite | 采用 sql 重写,支持单表多租户模式,逻辑删除,数据权限功能 |
| SAGA(实验) | BeetSQL 的 SAGA 是实现,用 SAGA 微服务事务 |
使用加速扩展性能优化结果:能达到近一半手写 JDBC 的性能
| 查询 | 测试内容 | BeetlSQL(ops/ms) | 纯 jdbc | mybatis | JPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| beetlsqlExecuteJdbc | 直接执行 JDBC | 318 | 678 | / | 64 |
| beetlsqlExecuteTemplate | 执行 SQL 模板 | 268 | / | 44 | 66 |
| beetlsqlFile | SQL 存放在文件统一管理 | 266 | / | 41 | / |
| beetlsqlInsert | 插入一条 | 129 | 248 | 43 | 59 |
| beetlsqlGetAll | 获取所有数据 | 13 | 40 | 4 | 5 |
| beetlsqlLambdaQuery | Java 函数编写 SQL 执行查询 | 196 | / | 9 | / |
| beetlsqlPageQuery | 翻页查询 | 159 | / | 17 | 59 |
| beetlsqlSelectById | 查询一条 | 259 | 670 | 43 | 61 |
BeetlSQL 3.x 使用说明,当前版本](https://www.kancloud.cn/xiandafu/beetlsql3_guide)
社区提供的文档 https://beetlsql-doc.vercel.app
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ibeetl</groupId>
<artifactId>beetlsql</artifactId>
<version>3.${version}</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>com.ibeetl</groupId>
<artifactId>beetlsql</artifactId>
<version>2.13.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>- 你不想把精力浪费在简单据库增删改查上?BeetlSQL 内置数据库的CRUD功能
- 你是属于以SQL为中心的程序员派别。BeetlSQL提供了较好的SQL管理,以及内置大量SQL
- 你是对代码可维护性有高要求的架构师?BeetlSQL的设计目的就是尽可能提高数据库访问代码可维护性
- 平台级产品需要跨库,支持各种客户数据库的?BeetlSQL 支持各种库,程序员编写一次,能运行到各种数据库
- 系统需要连接多种库,比如连接商品库,连接订单库,或者设备基本信息在MySQL,设备数据在Clickhouse里。BeetlSQL很容易支持各种库,并能一统一的方式使用
- 系统初期单库单表,长期需要多库多表?BeetlSQL很容易实现多库多表而不需要程序员过多关注。
git clone https://gitee.com/xiandafu/beetlsql
mvn clean package
# 如果想修改源码
mvn clean install 注意:BeetlSQL3 集成了Spring,以及支持大数据等,就算配置了国内镜像,也可能需要很长时间下载大数据依赖包,为了让编译快速通过,你需要进入pom.xml ,屏蔽sql-integration,sql-db-support,sql-jmh三个模块
<modules>
<!--核心功能 -->
<module>sql-core</module>
<module>sql-mapper</module>
<module>sql-util</module>
<module>sql-fetch</module>
<!-- 打包到一起 -->
<module>beetlsql</module>
<module>sql-gen</module>
<module>sql-test</module>
<module>sql-samples</module>
<module>sql-xml</module>
<module>sql-saga</module>
<!-- 集成和扩展太多的数据库,可以被屏蔽,以加速项目下载jar -->
<!-- <module>sql-integration</module>-->
<!-- <module>sql-jmh</module>-->
<!-- <module>sql-db-support</module>-->
</modules>
可以从模块sql-samples中找得到所有例子,或者从sql-test 中运行单元测试例子,或者在sql-integration 中的各个框架单元测试中找到相关例子。所有例子都是基于H2内存数据库,可以反复运行
以sql-samples为例子
sql-samples 又包含了三个模块大约100个例子
- quickstart: BeetlSQL基础使用例子,可以快速了解BeetlSQL3
- usuage: BeetlSQL所有API和功能
- plugin:BeetlSQL高级扩展实例
以usage模块为例子,包含如下代码
- S01MapperSelectSample 15个例子, mapper中的查询演示
- S02MapperUpdateSample 11个例子, mapper中更新操作
- S03MapperPageSample 3个例子,mapper中的翻页查询
- S04QuerySample 9个例子,Query查询
- S05QueryUpdateSample 3个例子,Query完成update操作
- S06SelectSample 14个例子,SQLManager 查询API
- S07InsertSample 8个例子,SQLManager 插入新数据API,主键生成
- S08UpdateSample 6个例子,更新数据
- S09JsonMappingSample 5个例子, json配置映射
- S10FetchSample 2个例子,关系映射
- S11BeetlFunctionSample 2个例子,自定义sql脚本的方法
BeetlSQL提供了saga事物管理一种思路,但目前还是试验版本,欢迎不怕死的人尝试,和我一起完善这部分,其例子可以在saga模块的单元测试中找到
UserEntity user = sqlManager.unique(UserEntity.class,1);
user.setName("ok123");
sqlManager.updateById(user);
UserEntity newUser = new UserEntity();
newUser.setName("newUser");
newUser.setDepartmentId(1);
sqlManager.insert(newUser);输出日志友好,可反向定位到调用的代码
┏━━━━━ Debug [user.selectUserAndDepartment] ━━━
┣ SQL: select * from user where 1 = 1 and id=?
┣ 参数: [1]
┣ 位置: org.beetl.sql.test.QuickTest.main(QuickTest.java:47)
┣ 时间: 23ms
┣ 结果: [1]
┗━━━━━ Debug [user.selectUserAndDepartment] ━━━
String sql = "select * from user where id=?";
Integer id = 1;
SQLReady sqlReady = new SQLReady(sql,new Object[id]);
List<UserEntity> userEntities = sqlManager.execute(sqlReady,UserEntity.class);
//Map 也可以作为输入输出参数
List<Map> listMap = sqlManager.execute(sqlReady,Map.class);String sql = "select * from user where department_id=#{id} and name=#{name}";
UserEntity paras = new UserEntity();
paras.setDepartmentId(1);
paras.setName("lijz");
List<UserEntity> list = sqlManager.execute(sql,UserEntity.class,paras);
String sql = "select * from user where id in ( #{join(ids)} )";
List list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5); Map paras = new HashMap();
paras.put("ids", list);
List<UserEntity> users = sqlManager.execute(sql, UserEntity.class, paras);支持重构
LambdaQuery<UserEntity> query = sqlManager.lambdaQuery(UserEntity.class);
List<UserEntity> entities = query.andEq(UserEntity::getDepartmentId,1)
.andIsNotNull(UserEntity::getName).select();//访问user.md#select
SqlId id = SqlId.of("user","select");
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","n");
List<UserEntity> list = sqlManager.select(id,UserEntity.class,map);支持像mybatis那样复杂的映射
- 自动映射
@Data
@ResultProvider(AutoJsonMapper.class)
public static class MyUserView {
Integer id;
String name;
DepartmentEntity dept;
}- 配置映射,比MyBatis更容易理解,报错信息更详细
{
"id": "id",
"name": "name",
"dept": {
"id": "dept_id",
"name": "dept_name"
},
"roles": {
"id": "r_id",
"name": "r_name"
}
}@SqlResource("user") /*sql文件在user.md里*/
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<UserEntity> {
@Sql("select * from user where id = ?")
UserEntity queryUserById(Integer id);
@Sql("update user set name=? where id = ?")
@Update
int updateName(String name,Integer id);
@Template("select * from user where id = #{id}")
UserEntity getUserById(Integer id);
@SpringData/*Spring Data风格*/
List<UserEntity> queryByNameOrderById(String name);
/**
* 可以定义一个default接口
* @return
*/
default List<DepartmentEntity> findAllDepartment(){
Map paras = new HashMap();
paras.put("exlcudeId",1);
List<DepartmentEntity> list = getSQLManager().execute("select * from department where id != #{exlcudeId}",DepartmentEntity.class,paras);
return list;
}
/**
* 调用sql文件user.md#select,方法名即markdown片段名字
* @param name
* @return
*/
List<UserEntity> select(String name);
/**
* 翻页查询,调用user.md#pageQuery
* @param deptId
* @param pageRequest
* @return
*/
PageResult<UserEntity> pageQuery(Integer deptId, PageRequest pageRequest);
@SqlProvider(provider= S01MapperSelectSample.SelectUserProvider.class)
List<UserEntity> queryUserByCondition(String name);
@SqlTemplateProvider(provider= S01MapperSelectSample.SelectUs
List<UserEntity> queryUserByTemplateCondition(String name);
@Matcher /*自己定义个Matcher注解也很容易*/
List<UserEntity> query(Condition condition,String name);
}你看到的这些用在Mapper上注解都是可以自定义,自己扩展的
可以在查询后根据Fetch注解再次获取相关对象,实际上@FetchOne和 @FetchMany是自定义的,用户可自行扩展
@Data
@Table(name="user")
@Fetch
public static class UserData {
@Auto
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer departmentId;
@FetchOne("departmentId")
private DepartmentData dept;
}
/**
* 部门数据使用"b" sqlmanager
*/
@Data
@Table(name="department")
@Fetch
public static class DepartmentData {
@Auto
private Integer id;
private String name;
@FetchMany("departmentId")
private List<UserData> users;
}可以自行扩展ConditionalSQLManager的decide方法,来决定使用哪个SQLManager
SQLManager a = SampleHelper.init();
SQLManager b = SampleHelper.init();
Map<String, SQLManager> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", a);
map.put("b", b);
SQLManager sqlManager = new ConditionalSQLManager(a, map);
//不同对象,用不同sqlManager操作,存入不同的数据库
UserData user = new UserData();
user.setName("hello");
user.setDepartmentId(2);
sqlManager.insert(user);
DepartmentData dept = new DepartmentData();
dept.setName("dept");
sqlManager.insert(dept);使用注解 @TargetSQLManager来决定使用哪个SQLManger
@Data
@Table(name = "department")
@TargetSQLManager("b")
public static class DepartmentData {
@Auto
private Integer id;
private String name;
}这样好处是方便数据库DBA与程序员沟通
public static class SqlIdAppendInterceptor implements Interceptor{
@Override
public void before(InterceptorContext ctx) {
ExecuteContext context = ctx.getExecuteContext();
String jdbcSql = context.sqlResult.jdbcSql;
String info = context.sqlId.toString();
//为发送到数据库的sql增加一个注释说明,方便数据库dba能与开发人员沟通
jdbcSql = "/*"+info+"*/\n"+jdbcSql;
context.sqlResult.jdbcSql = jdbcSql;
}
}可以使用内置的代码生成框架生成代码何文档,也可以自定义的,用户可自行扩展SourceBuilder类
List<SourceBuilder> sourceBuilder = new ArrayList<>();
SourceBuilder entityBuilder = new EntitySourceBuilder();
SourceBuilder mapperBuilder = new MapperSourceBuilder();
SourceBuilder mdBuilder = new MDSourceBuilder();
//数据库markdown文档
SourceBuilder docBuilder = new MDDocBuilder();
sourceBuilder.add(entityBuilder);
sourceBuilder.add(mapperBuilder);
sourceBuilder.add(mdBuilder);
sourceBuilder.add(docBuilder);
SourceConfig config = new SourceConfig(sqlManager,sourceBuilder);
//只输出到控制台
ConsoleOnlyProject project = new ConsoleOnlyProject();
String tableName = "USER";
config.gen(tableName,project); GroupTemplate groupTemplate = groupTemplate();
groupTemplate.registerFunction("nextDay",new NextDayFunction());
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("date",new Date());
String sql = "select * from user where create_time is not null and create_time<#{nextDay(date)}";
List<UserEntity> count = sqlManager.execute(sql,UserEntity.class,map);nextDay函数是一个Beetl函数,非常容易定义,非常容易在sql模板语句里使用
public static class NextDayFunction implements Function {
@Override
public Object call(Object[] paras, Context ctx) {
Date date = (Date) paras[0];
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(date);
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR, 1); // 今天+1天
return c.getTime();
}
}根据ID或者上下文自动分表,toTable是定义的一个Beetl函数,
static final String USER_TABLE="${toTable('user',id)}";
@Data
@Table(name = USER_TABLE)
public static class MyUser {
@AssignID
private Integer id;
private String name;
}定义一个Jackson注解,@Builder是注解的注解,表示用Builder指示的类来解释执行,可以看到BeetlSQL的注解可扩展性就是来源于@Build注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Builder(JacksonConvert.class)
public @interface Jackson {
}定义一个@Tenant 放在POJO上,BeetlSQL执行时候会给SQL添加额外参数,这里同样使用了@Build注解
/**
* 组合注解,给相关操作添加额外的租户信息,从而实现根据租户分表或者分库
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Builder(TenantContext.class)
public @interface Tenant {
}使用XML而不是JSON作为映射
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Builder(ProviderConfig.class)
public @interface XmlMapping {
String path() default "";
}参考源码例子 PluginAnnotationSample了解如何定义自定的注解,实际上BeetlSQL有一半的注解都是通过核心注解扩展出来的
BeetlSQL除了集成传统的事务管理器外,也提供Saga事务支持,支持多库事务和微服务事务。 其原理是自动为每个操作提供反向操作,如insert的反向操作是deleteById,并把这些操作作为任务交给Saga—Server调度。实现了通过Kafka作为客户端(各个APP)与SagaServer 交互的媒介保证任务可靠传递并最终被系统执行。
String orderAddUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:8081/order/item/{orderId}/{userId}/{fee}";
String userBalanceUpdateUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:8082/user/fee/{orderId}/{userId}/{fee}";
..........
SagaContext sagaContext = SagaContext.sagaContextFactory.current();
try {
sagaContext.start(gid);
//模拟调用俩个微服务,订单和用户
rest.postForEntity(orderAddUrl, null,String.class, paras);
rest.postForEntity(userBalanceUpdateUrl, null,String.class, paras);
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("模拟失败,查询saga-server 看效果");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("error " + e.getMessage());
log.info("start rollback " + e.getMessage());
sagaContext.rollback();
return e.getMessage();
}以用户系统为例(源码是DemoController),userBalanceUpdateUrl对应如下扣费逻辑
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Transactional(propagation= Propagation.NEVER)
public void update(String orderId,String userId,Integer fee){
SagaContext sagaContext = SagaContext.sagaContextFactory.current();
try{
sagaContext.start(orderId);
UserEntity user = userMapper.unique(userId);
user.setBalance(user.getBalance()-fee);
userMapper.updateById(user);
sagaContext.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
sagaContext.rollback();
}
}这里的UserMapper实际上是SagaMapper子类(而不是BaseMapper),会为每个操作提供反向操作
public interface SagaMapper<T> {
/** sega 改造的接口**/
@AutoMapper(SagaInsertAMI.class)
void insert(T entity);
@AutoMapper(SagaUpdateByIdAMI.class)
int updateById(T entity);
@AutoMapper(SagaDeleteByIdAMI.class)
int deleteById(Object key);
}除了SQLManager和ClassAnnotations,任何一部分都可以扩展